Genetic influences in emotional dysfunction and alcoholism-related brain damage
- PMID: 18568071
- PMCID: PMC2416753
Genetic influences in emotional dysfunction and alcoholism-related brain damage
Abstract
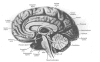
Alcoholism is a complex, multifactorial disorder involving problematic ethanol ingestion; it results from the interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Personality, likewise, is formed from a combination of inherited and acquired influences. Because selected dimensions of emotional temperament are associated with distinct neurochemical substrates contributing to specific personality phenotypes, certain aspects of abnormal emotional traits in alcoholics may be inherited. Emotions involve complex subjective experiences engaging multiple brain regions, most notably the cortex, limbic system, and cerebellum. Results of in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and post-mortem neuropathological studies of alcoholics indicate that the greatest cortical loss occurs in the frontal lobes, with concurrent thinning of the corpus callosum. Additional damage has been documented for the amygdala and hippocampus, as well as in the white matter of the cerebellum. All of the critical areas of alcoholism-related brain damage are important for normal emotional functioning. When changes occur in these brain regions, either as a consequence of chronic ethanol abuse or from a genetic anomaly affecting temperament and/or a vulnerability to alcoholism, corresponding changes in emotional functions are to be expected. In alcoholics, such changes have been observed in their perception and evaluation of emotional facial expressions, interpretation of emotional intonations in vocal utterances, and appreciation of the meaning of emotional materials.
Keywords: alcoholism; emotional dysfunction; genetic influences; personality.
Figures

References
-
- Abdollah S, Catlin MC, Brien JF. Ethanol neuro-behavioural teratogenesis in the guinea pig: behavioural dysfunction and hippocampal morphological change. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1993;71:776–82. - PubMed
-
- Adamson MD, Kennedy J, Petronis A, et al. DRD2 dopamine receptor genotype and CSF monoamine metabolites in Finnish alcoholics and controls. Am J Med Genet. 1995;60:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Jansari A, Tranel D. Hemispheric perception of emotional valence from facial expressions. Neuropsychology. 2001;15:516–24. - PubMed
-
- Agartz I, Momenam R, Rawlings RR, et al. Hippocampal volume in patients with alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:356–63. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
