Cigarette smoke-induced neurogenic inflammation is mediated by alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes and the TRPA1 receptor in rodents
- PMID: 18568077
- PMCID: PMC2430498
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI34886
Cigarette smoke-induced neurogenic inflammation is mediated by alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes and the TRPA1 receptor in rodents
Abstract
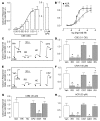
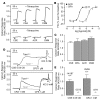
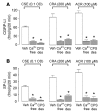
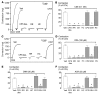
Cigarette smoke (CS) inhalation causes an early inflammatory response in rodent airways by stimulating capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons that express transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 1 (TRPV1) through an unknown mechanism that does not involve TRPV1. We hypothesized that 2 alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes present in CS, crotonaldehyde and acrolein, induce neurogenic inflammation by stimulating TRPA1, an excitatory ion channel coexpressed with TRPV1 on capsaicin-sensitive nociceptors. We found that CS aqueous extract (CSE), crotonaldehyde, and acrolein mobilized Ca2+ in cultured guinea pig jugular ganglia neurons and promoted contraction of isolated guinea pig bronchi. These responses were abolished by a TRPA1-selective antagonist and by the aldehyde scavenger glutathione but not by the TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine or by ROS scavengers. Treatment with CSE or aldehydes increased Ca2+ influx in TRPA1-transfected cells, but not in control HEK293 cells, and promoted neuropeptide release from isolated guinea pig airway tissue. Furthermore, the effect of CSE and aldehydes on Ca2+ influx in dorsal root ganglion neurons was abolished in TRPA1-deficient mice. These data identify alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes as the main causative agents in CS that via TRPA1 stimulation mediate airway neurogenic inflammation and suggest a role for TRPA1 in the pathogenesis of CS-induced diseases.
Figures

Comment in
-
How irritating: the role of TRPA1 in sensing cigarette smoke and aerogenic oxidants in the airways.J Clin Invest. 2008 Jul;118(7):2383-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI36111. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18568080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geppetti, P., and Holzer, P. 1996. Neurogenic inflammation. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, USA. 256 pp.
-
- Szallasi A., Blumberg P.M. Vanilloid (capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:159–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

