Small molecule inhibition of microbial natural product biosynthesis-an emerging antibiotic strategy
- PMID: 18568158
- PMCID: PMC2587208
- DOI: 10.1039/b702780j
Small molecule inhibition of microbial natural product biosynthesis-an emerging antibiotic strategy
Abstract
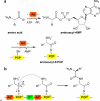
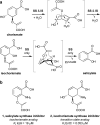
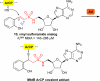
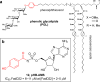
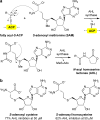
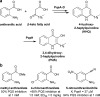
A variety of natural products modulate critical biological processes in the microorganisms that produce them. Thus, inhibition of the corresponding natural product biosynthesis pathways represents a promising avenue to develop novel antibiotics. In this tutorial review, we describe several recent examples of designed small molecule inhibitors of microbial natural product biosynthesis and their use in evaluating this emerging antibiotic strategy.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

