FOXG1 is responsible for the congenital variant of Rett syndrome
- PMID: 18571142
- PMCID: PMC2443837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.05.015
FOXG1 is responsible for the congenital variant of Rett syndrome
Abstract
Rett syndrome is a severe neurodevelopmental disease caused by mutations in the X-linked gene encoding for the methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2. Here, we report the identification of FOXG1-truncating mutations in two patients affected by the congenital variant of Rett syndrome. FOXG1 encodes a brain-specific transcriptional repressor that is essential for early development of the telencephalon. Molecular analysis revealed that Foxg1 might also share common molecular mechanisms with MeCP2 during neuronal development, exhibiting partially overlapping expression domain in postnatal cortex and neuronal subnuclear localization.
Figures
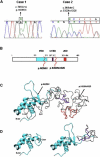
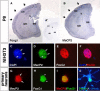
References
-
- Chahrour M., Zoghbi H.Y. The story of Rett syndrome: from clinic to neurobiology. Neuron. 2007;56:422–437. - PubMed
-
- Hagberg B.A., Skjeldal O.H. Rett variants: A suggested model for inclusion criteria. Pediatr. Neurol. 1994;11:5–11. - PubMed
-
- De Bona C., Zappella M., Hayek G., Meloni I., Vitelli F., Bruttini M., Cusano R., Loffredo P., Longo I., Renieri A. Preserved speech variant is allelic of classic Rett syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2000;8:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Tao J., Van Esch H., Hagedorn-Greiwe M., Hoffmann K., Moser B., Raynaud M., Sperner J., Fryns J., Schwinger E., Gecz J. Mutations in the X-linked cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5/STK9) gene are associated with severe neurodevelopmental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004;75:1149–1154. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

