Mechanism of Ca2+-influx and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV activity during in utero hypoxia in cerebral cortical neuronal nuclei of the guinea pig fetus at term
- PMID: 18571321
- PMCID: PMC2758039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.095
Mechanism of Ca2+-influx and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV activity during in utero hypoxia in cerebral cortical neuronal nuclei of the guinea pig fetus at term
Abstract
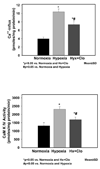
Previously we showed that following hypoxia there is an increase in nuclear Ca(2+)-influx and Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV activity (CaMK IV) in the cerebral cortex of term guinea pig fetus. The present study tests the hypothesis that clonidine administration will prevent hypoxia-induced increased neuronal nuclear Ca(2+)-influx and increased CaMK IV activity, by blocking high-affinity Ca(2+)-ATPase. Studies were conducted in 18 pregnant guinea pigs at term, normoxia (Nx, n=6), hypoxia (Hx, n=6) and clonidine with Hx (Hx+Clo, n=6). The pregnant guinea pig was exposed to a decreased FiO(2) of 0.07 for 60 min. Clonidine, an imidazoline inhibitor of high-affinity Ca(2+)-ATPase, was administered 12.5 microg/kg IP 30 min prior to hypoxia. Hypoxia was determined biochemically by ATP and phosphocreatine (PCr) levels. Nuclei were isolated and ATP-dependent (45)Ca(2+)-influx was determined. CaMK IV activity was determined by (33)P-incorporation into syntide 2 for 2 min at 37 degrees C in a medium containing 50mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 2mM DTT, 40muM syntide 2, 0.2mM (33)P-ATP, 10mM magnesium acetate, 5 microM PKI 5-24, 2 microM PKC 19-36 inhibitor peptides, 1 microM microcystine LR, 200 microM sodium orthovanadate and either 1mM EGTA (for CaMK IV-independent activity) or 0.8mM CaCl(2) and 1mM calmodulin (for total activity). ATP (mumoles/gbrain) values were significantly different in the Nx (4.62+/-0.2), Hx (1.65+/-0.2, p<0.05 vs. Nx), and Hx+Clo (1.92+/-0.6, p<0.05 vs. Nx). PCr (mumoles/g brain) values in the Nx (3.9+/-0.1), Hx (1.10+/-0.3, p<0.05 vs. Nx), and Hx+Clo (1.14+/-0.3, p<0.05 vs. Nx). There was a significant difference between nuclear Ca(2+)-influx (pmoles/mg protein/min) in Nx (3.98+/-0.4), Hx (10.38+/-0.7, p<0.05 vs. Nx), and Hx+Clo (7.35+/-0.9, p<0.05 vs. Nx, p<0.05 vs. Hx), and CaM KIV (pmoles/mg protein/min) in Nx (1314.00+/-195.4), Hx (2315.14+/-148.5, p<0.05 vs. Nx), and Hx+Clo (1686.75+/-154.3, p<0.05 vs. Nx, p<0.05 vs. Hx). We conclude that the mechanism of hypoxia-induced increased nuclear Ca(2+)-influx is mediated by high-affinity Ca(2+)-ATPase and that CaMK IV activity is nuclear Ca(2+)-influx-dependent. We speculate that hypoxia-induced alteration of high-affinity Ca(2+)-ATPase is a key step that triggers nuclear Ca(2+)-influx, leading to CREB protein-mediated increased expression of apoptotic proteins and hypoxic neuronal death.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear Ca(++)-influx, Ca (++)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV activity and CREB protein phosphorylation during post-hypoxic reoxygenation in neuronal nuclei of newborn piglets: the role of nitric oxide.Neurochem Res. 2006 Dec;31(12):1463-71. doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9204-x. Epub 2006 Nov 8. Neurochem Res. 2006. PMID: 17091402
-
Effect of post-hypoxic MgSO(4) administration in utero on Ca(2+)-influx and Ca(2+)/calmodulin kinase IV activity in cortical neuronal nuclei.Neurosci Lett. 2005 Sep 30;386(2):127-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.05.064. Neurosci Lett. 2005. PMID: 16006037
-
Nitric oxide-mediated Ca++-influx in neuronal nuclei and cortical synaptosomes of normoxic and hypoxic newborn piglets.Neurosci Lett. 2002 Jan 25;318(2):93-7. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(01)02484-3. Neurosci Lett. 2002. PMID: 11796194
-
Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) during hypoxia in cerebral cortical nuclei of guinea pig fetus at term: role of nitric oxide.Neurosci Lett. 2008 Jul 4;439(1):94-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.02.037. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Neurosci Lett. 2008. PMID: 18511197
-
Nuclear mechanisms of hypoxic cerebral injury in the newborn.Clin Perinatol. 2004 Mar;31(1):91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2004.03.007. Clin Perinatol. 2004. PMID: 15183659 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Src Kinase inhibition on Cytochrome c, Smac/DIABLO and Apoptosis Inducing Factor (AIF) Following Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia in Newborn Piglets.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 30;7(1):16664. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16983-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29192254 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition Reverses Cellular and Transcriptomic Alterations Induced by Hypoxia in the Neonatal Piglet Brain.iScience. 2020 Nov 4;23(12):101766. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101766. eCollection 2020 Dec 18. iScience. 2020. PMID: 33294779 Free PMC article.
-
Guinea pig models for translation of the developmental origins of health and disease hypothesis into the clinic.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(23):5535-5569. doi: 10.1113/JP274948. Epub 2018 May 30. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29633280 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Concurrent Src Kinase Inhibition with Short-Duration Hypothermia on Ca2+/Calmodulin Kinase IV Activity and Neuropathology after Hypoxia-Ischemia in the Newborn Swine Brain.Neonatology. 2018;113(1):37-43. doi: 10.1159/000480067. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Neonatology. 2018. PMID: 29024930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedin N, Ashraf Q, Mishra OP, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M. Effect of hypoxia on the expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins in neuronal nuclei of the guinea pig fetus during gestation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2005;156:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Peppiatt CM, Prothero LS, MacKenzie L, De Smet P, Travers M, Tovey SC, Seo JT, Berridge MJ, Ciccolini F, Lipp P. Calcium signalling–an overview. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2001;12:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Braun AP, Schulman H. The multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: from form to function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:417–445. - PubMed
-
- De Koninck P, Schulman H. Sensitivity of CaM kinase II to the frequency of Ca++ oscillations. Science. 1998;279:227–230. - PubMed
-
- Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Akhter W, Mishra OP. Hypoxia-induced Ca2+-influx in cerebral cortical neuronal nuclei of newborn piglets. Neurosci Lett. 2003;342:119–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

