High-sensitivity analysis of glycosphingolipids by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight imaging mass spectrometry on transfer membranes
- PMID: 18571485
- PMCID: PMC2551320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.06.001
High-sensitivity analysis of glycosphingolipids by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight imaging mass spectrometry on transfer membranes
Abstract
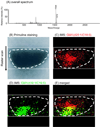
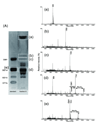
Glycosphingolipids are ubiquitous constituents of cells. Yet there is still room for improvement in the techniques for analyzing glycosphingolipids. Here we report our highly sensitive and convenient analytical technology with imaging mass spectrometry for detailed structural analysis of glycosphingolipids. We were able to determine detailed ceramide structures; i.e., both the sphingosine base and fatty acid, by MS/MS/MS analysis on a PVDF membrane with 10 pmol of GM1, with which only faint bands were visible by primuline staining. The limit of detection was approximately 1 pmol of GM1, which is lower than the value in the conventional reports (10 pmol).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structural characterization of neutral glycosphingolipids by thin-layer chromatography coupled to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight MS/MS.Anal Chem. 2006 Aug 15;78(16):5736-43. doi: 10.1021/ac0605501. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16906718
-
Direct matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipids on thin layer chromatographic plates and transfer membranes.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1999;13(18):1838-49. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(19990930)13:18<1838::AID-RCM726>3.0.CO;2-9. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1999. PMID: 10482898
-
Convenient structural analysis of glycosphingolipids using MALDI-QIT-TOF mass spectrometry with increased laser power and cooling gas flow.J Biochem. 2006 Apr;139(4):771-7. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj090. J Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16672278
-
Glycosphingolipid structural analysis and glycosphingolipidomics.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:300-69. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05012-3. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413319 Review.
-
Advances on the compositional analysis of glycosphingolipids combining thin-layer chromatography with mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2010 May-Jun;29(3):425-79. doi: 10.1002/mas.20253. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2010. PMID: 19609886 Review.
Cited by
-
Bio-recognition and functional lipidomics by glycosphingolipid transfer technology.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2013;89(7):302-20. doi: 10.2183/pjab.89.302. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23883610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MALDI imaging of lipid biochemistry in tissues by mass spectrometry.Chem Rev. 2011 Oct 12;111(10):6491-512. doi: 10.1021/cr200280p. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 21942646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Developments and applications of mass microscopy.Med Mol Morphol. 2010 Mar;43(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s00795-009-0489-0. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Med Mol Morphol. 2010. PMID: 20339999 Review.
-
Lipidomics analysis revealed the phospholipid compositional changes in muscle by chronic exercise and high-fat diet.Sci Rep. 2013 Nov 20;3:3267. doi: 10.1038/srep03267. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 24253370 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging mass spectrometry: principle and application.Biophys Rev. 2009 Sep;1(3):131. doi: 10.1007/s12551-009-0015-6. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Biophys Rev. 2009. PMID: 28509996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

