B cell receptor accessory molecules in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus
- PMID: 18572245
- PMCID: PMC2561914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.05.008
B cell receptor accessory molecules in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus
Abstract
B cell receptor (BCR) accessory molecules CD79a and CD79b homologs were identified in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Both are found as single copy genes that encode proteins containing a signal peptide, an extracellular immunoglobulin domain, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail containing an immune-receptor tyrosine-dased activation motif (ITAM). IpCD79a and IpCD79b transcripts correlate well with IgM message expression. They are highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL) enriched in membrane (m) IgM+ cells and catfish clonal B cell lines, but not in catfish clonal T cells, indicating that IpCD79a and IpCD79b expression is B cell restricted. Studies using catfish clonal B cells (3B11) transfected with constructs encoding epitope-tagged IpCD79a and IpCD79b revealed that IpCD79a was expressed as a 45 kDa protein and IpCD79b was expressed as a 32 kDa protein. Furthermore, co-immunoprecipitations of epitope-tagged CD79 proteins demonstrate that these molecules are non-covalently associated with mIgM. These data correlate with some of the previous immunoprecipitation data demonstrating that catfish mIgM associates with proteins of 45 and 32 kDa.
Figures





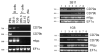


References
-
- Hombach J, Tsubata T, Leclercq L, Stappert H, Reth M. Molecular components of the B-cell antigen receptor complex of the IgM class. Nature. 1990;343:760–2. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo T, Kimoto M, Sakaguchi N. Direct identification of the putative surface IgM receptor-associated molecule encoded by murine B cell-specific mb-1 gene. J Immunol. 1991;146:1584–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

