Cell adhesion and polarisation on molecularly defined spacing gradient surfaces of cyclic RGDfK peptide patches
- PMID: 18572273
- PMCID: PMC2564985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.03.011
Cell adhesion and polarisation on molecularly defined spacing gradient surfaces of cyclic RGDfK peptide patches
Abstract
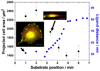
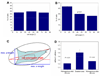
In vivo cell migration and location are orchestrally guided by soluble and bound chemical gradients. Here, gradients of extracellular matrix molecules are formed synthetically by the combination of a surface nanopatterning technique called block copolymer nanolithography (BCN) and a biofunctionalisation technique. A modified substrate dip-coating process of BCN allows for the formation of precise molecular gradients of cyclic RGDfK peptide patches at interfaces, which are presented to cells for testing cell adhesion and polarisation. Surfaces formed by BCN consist of hexagonally ordered gold dot patterns with a gradient in particle spacing. Each dot serves as a chemical anchor for the binding of cyclic RGDfK peptides, which are specifically recognised by alpha(v)beta(3) integrins. Due to steric hindrance only up to one integrin binds to one functionalised gold dot which forms a peptide patch spacing. We demonstrate how cell morphology, adhesion area, actin and vinculin distribution as well as cell body polarisation are influenced by the peptide patch spacing gradient. As a consequence, these gradients of adhesive ligands induce cell orientation towards smaller particle spacing when the gradient strength is 15nm/mm at least. This implicates that an adherent cell's sensitivity to differentiate between ligand patch spacing is approximately 1nm across the cell body.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of integrin function by nanopatterned adhesive interfaces.Chemphyschem. 2004 Mar 19;5(3):383-8. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200301014. Chemphyschem. 2004. PMID: 15067875
-
Cellular unbinding forces of initial adhesion processes on nanopatterned surfaces probed with magnetic tweezers.Nano Lett. 2006 Mar;6(3):398-402. doi: 10.1021/nl052168u. Nano Lett. 2006. PMID: 16522030
-
Lateral spacing of integrin ligands influences cell spreading and focal adhesion assembly.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;85(3-4):219-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.09.011. Epub 2005 Oct 10. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16546564
-
Structure and function of focal adhesions.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;24(1):116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22138388 Review.
-
Cell matrix adhesions in cancer: The proteins that form the glue.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):48471-48487. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17265. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28476046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin nanoclusters can bridge thin matrix fibres to form cell-matrix adhesions.Nat Mater. 2019 Dec;18(12):1366-1375. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0460-y. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Nat Mater. 2019. PMID: 31477904 Free PMC article.
-
NANOPATTERNED INTERFACES FOR CONTROLLING CELL BEHAVIOR.Nano Life. 2010 Mar;1(1-amp 2):63-77. doi: 10.1142/S1793984410000055. Nano Life. 2010. PMID: 25383101 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial growth of oxide nanoscaffolds and its influence in osteoblast cell adhesion.J Appl Phys. 2012 May 15;111(10):102810-1028107. doi: 10.1063/1.4714727. Epub 2012 May 17. J Appl Phys. 2012. PMID: 22670064 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving insights in cell-matrix interactions: elucidating how non-soluble properties of the extracellular niche direct stem cell fate.Acta Biomater. 2015 Jan;11:3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.09.038. Epub 2014 Oct 5. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25266503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gradient biomaterials and their influences on cell migration.Interface Focus. 2012 Jun 6;2(3):337-55. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0124. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Interface Focus. 2012. PMID: 23741610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold M. PhD thesis. Heidelberg, Germany: University of Heidelberg; 2006. Molecularly defined nanostructured interfaces as tools for the regulation and measurement of functional length scales in cell adhesion mediating protein clusters.
-
- Arnold M, Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Glass R, Blümmel J, Eck W, Kanthlener M, Kessler H, Spatz JP. Activation of integrin function by nanopatterned adhesive interfaces. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2004;5:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Blümmel J, Perschmann N, Aydin D, Drinjakovic J, Surrey T, López-García, M, Kessler H, Spatz JP. Protein repellent properties of covalently attached PEG coatings on nanostructured SiO2 based interfaces. Biomaterials. 2007;28:4739–4747. - PubMed
-
- Carter SB. Principles of cell motility: the direction of cell movement and cancer invasion. Nature. 1965;208:1183–1187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

