Evolution of a behavior-linked microsatellite-containing element in the 5' flanking region of the primate AVPR1A gene
- PMID: 18573213
- PMCID: PMC2483724
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-180
Evolution of a behavior-linked microsatellite-containing element in the 5' flanking region of the primate AVPR1A gene
Abstract
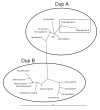
Background: The arginine vasopressin V1a receptor (V1aR) modulates social cognition and behavior in a wide variety of species. Variation in a repetitive microsatellite element in the 5' flanking region of the V1aR gene (AVPR1A) in rodents has been associated with variation in brain V1aR expression and in social behavior. In humans, the 5' flanking region of AVPR1A contains a tandem duplication of two approximately 350 bp, microsatellite-containing elements located approximately 3.5 kb upstream of the transcription start site. The first block, referred to as DupA, contains a polymorphic (GT)25 microsatellite; the second block, DupB, has a complex (CT)4-(TT)-(CT)8-(GT)24 polymorphic motif, known as RS3. Polymorphisms in RS3 have been associated with variation in sociobehavioral traits in humans, including autism spectrum disorders. Thus, evolution of these regions may have contributed to variation in social behavior in primates. We examined the structure of these regions in six ape, six monkey, and one prosimian species.
Results: Both tandem repeat blocks are present upstream of the AVPR1A coding region in five of the ape species we investigated, while monkeys have only one copy of this region. As in humans, the microsatellites within DupA and DupB are polymorphic in many primate species. Furthermore, both single (lacking DupB) and duplicated alleles (containing both DupA and DupB) are present in chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) populations with allele frequencies of 0.795 and 0.205 for the single and duplicated alleles, respectively, based on the analysis of 47 wild-caught individuals. Finally, a phylogenetic reconstruction suggests two alternate evolutionary histories for this locus.
Conclusion: There is no obvious relationship between the presence of the RS3 duplication and social organization in primates. However, polymorphisms identified in some species may be useful in future genetic association studies. In particular, the presence of both single and duplicated alleles in chimpanzees provides a unique opportunity to assess the functional role of this duplication in contributing to variation in social behavior in primates. While our initial studies show no signs of directional selection on this locus in chimps, pharmacological and genetic association studies support a potential role for this region in influencing V1aR expression and social behavior.
Figures



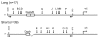
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

