Cost-effectiveness of ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 18573218
- PMCID: PMC2443361
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-7547-6-12
Cost-effectiveness of ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
Background: Intravitreal ranibizumab prevents vision loss and improves visual acuity in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration, but it is expensive, and efficacy beyond 2 years is uncertain.
Methods: We assessed the cost-effectiveness of ranibizumab compared with no ranibizumab over 10 years, using randomized trial efficacy data for the first 2 years, post-trial efficacy assumptions, and ranibizumab acquisition costs ranging from the wholesale price ($1,950 per dose) to the price of bevazicumab ($50), a similar molecule which may be equally efficacious. We used a computer simulation model to estimate the probability of blindness, the number of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), direct costs (in 2004 U.S. dollars), and cost-effectiveness ratios for a 67-year old woman. Costs and QALYs were discounted at 3% per year.
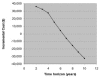
Results: The probability of blindness over 10 years was reduced from 56% to 34% if ranibizumab was efficacious for only 2 years, 27% if efficacy was maintained for a further 2 years only (base-case scenario), and 17% if visual acuity at 4 years was then sustained. It was cost-saving under all price assumptions, when caregiver costs were included. When caregiver costs were excluded, the cost per QALY for the base-case ranged from $5,600, assuming the bevazicumab price, to $91,900 assuming the wholesale ranibizumab price. The cost per QALY was < $50,000 when the cost of ranibizumab was less than $1000.
Conclusion: From a societal perspective, ranibizumab was cost-saving. From a health care funder's perspective, ranibizumab was an efficient treatment when it cost less than $1000 per dose.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenfeld PJ, Rich RM, Lalwani GA. Ranibizumab: Phase III clinical trial results. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2006;19:361–372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

