Mannitol enhances delivery of marrow stromal cells to the brain after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 18573239
- PMCID: PMC2712137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.080
Mannitol enhances delivery of marrow stromal cells to the brain after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
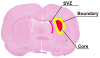
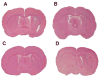
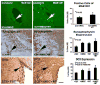
Previous studies show that intravascular injection of human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSCs) significantly improves neurological functional recovery in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that mannitol improves the efficiency of intraarterial MSC delivery (i.e., fewer injected cells required for therapeutic efficacy) after ICH. There were four post-ICH groups (N=9): group 1, negative control with only intraarterial injection of 1 million human fibroblasts in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS); group 2, intravenous injection of mannitol alone in PBS (1.5 g/kg); group 3, intraarterial injection of 1 million hBMSCs alone in PBS; and group 4, intravenous injection of mannitol (1.5 g/kg) in PBS followed by intraarterial injection of 1 million hBMSCs in PBS. Group 4 exhibited significantly improved neurological functional outcome as assessed by neurological severity score (NSS) and corner test scores. Immunohistochemical staining of group 4 suggested increased synaptogenesis, proliferating immature neurons, and neuronal migration. The number of hBMSCs recruited to the injured region increased strikingly in group 4. Tissue loss was notably reduced in group 4. In summary, the beneficial effects of intraarterial infusion of MSCs are amplified with intravenous injection of mannitol. Preadministration of mannitol significantly increases the number of hBMSCs located in the ICH region, improves histochemical parameters of neural regeneration, and reduces the anatomical and pathological consequences of ICH.
Figures
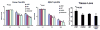

References
-
- Boulard G, Marguinaud E, Sesay M. Osmotic cerebral oedema: the role of plasma osmolarity and blood brain barrier. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2003;22:215–219. - PubMed
-
- Burke AM, Quest DO, Chien S, Cerri C. The effects of mannitol on blood viscosity. J Neurosurg. 1981;55:550–553. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Zhang X, Chopp M. Therapeutic benefit of intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2001a;189:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J, Chopp M. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2001b;32:2682–2688. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Zhang ZG, Li Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Jiang H, Zhang C, Lu M, Katakowski M, Feldkamp CS, Chopp M. Statins induce angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis after stroke. Ann Neurol. 2003;53:743–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

