Profiling the phospho-status of the BKCa channel alpha subunit in rat brain reveals unexpected patterns and complexity
- PMID: 18573811
- PMCID: PMC2577206
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800063-MCP200
Profiling the phospho-status of the BKCa channel alpha subunit in rat brain reveals unexpected patterns and complexity
Abstract
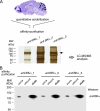
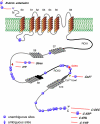
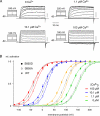
Molecular diversity of ion channel structure and function underlies variability in electrical signaling in nerve, muscle, and non-excitable cells. Protein phosphorylation and alternative splicing of pre-mRNA are two important mechanisms to generate structural and functional diversity of ion channels. However, systematic mass spectrometric analyses of in vivo phosphorylation and splice variants of ion channels in native tissues are largely lacking. Mammalian large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK(Ca)) channels are tetramers of alpha subunits (BKalpha) either alone or together with beta subunits, exhibit exceptionally large single channel conductance, and are dually activated by membrane depolarization and intracellular Ca(2+). The cytoplasmic C terminus of BKalpha is subjected to extensive pre-mRNA splicing and, as predicted by several algorithms, offers numerous phospho-acceptor amino acids. Here we use nanoflow liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry on BK(Ca) channels affinity-purified from rat brain to analyze in vivo BKalpha phosphorylation and splicing. We found 7 splice variations and identified as many as 30 Ser/Thr in vivo phosphorylation sites; most of which were not predicted by commonly used algorithms. Of the identified phosphosites 23 are located in the C terminus, four were found on splice insertions. Electrophysiological analyses of phospho- and dephosphomimetic mutants transiently expressed in HEK-293 cells suggest that phosphorylation of BKalpha differentially modulates the voltage- and Ca(2+)-dependence of channel activation. These results demonstrate that the pore-forming subunit of BK(Ca) channels is extensively phosphorylated in the mammalian brain providing a molecular basis for the regulation of firing pattern and excitability through dynamic modification of BKalpha structure and function.
Figures

References
-
- Hille, B. ( 2001) Ionic channels of excitable membranes, 3rd Ed., Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
-
- Shipston, M. J. ( 2001) Alternative splicing of potassium channels: a dynamic switch of cellular excitability. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 353–358 - PubMed
-
- Cantrell, A. R., and Catterall, W. A. ( 2001) Neuromodulation of Na+ channels: an unexpected form of cellular plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 397–407 - PubMed
-
- Coetzee, W. A., Amarillo, Y., Chiu, J., Chow, A., Lau, D., McCormack, T., Moreno, H., Nadal, M. S., Ozaita, A., Pountney, D., Saganich, M., Vega-Saenz de Miera, E., and Rudy, B. ( 1999) Molecular diversity of K+ channels. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 868, 233–285 - PubMed
-
- Fury, M., Marx, S. O., and Marks, A. R. ( 2002) Molecular BKology: the study of splicing and dicing. Sci STKE 2002, PE12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

