Engineering of halophilic enzymes: two acidic amino acid residues at the carboxy-terminal region confer halophilic characteristics to Halomonas and Pseudomonas nucleoside diphosphate kinases
- PMID: 18573868
- PMCID: PMC2525524
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.035725.108
Engineering of halophilic enzymes: two acidic amino acid residues at the carboxy-terminal region confer halophilic characteristics to Halomonas and Pseudomonas nucleoside diphosphate kinases
Abstract
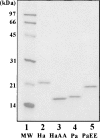
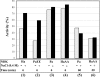
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase from Halomonas sp. 593 (HaNDK) exhibits halophilic characteristics. Residues 134 and 135 in the carboxy-terminal region of HaNDK are Glu-Glu, while those of its homologous counterpart of non-halophilic Pseudomonas NDK (PaNDK) are Ala-Ala. The double mutation, E134A-E135A, in HaNDK results in the loss of the halophilic characteristics, and, conversely, the double mutation of A134E-A135E in PaNDK confers halophilic characters to this enzyme, indicating that the charged state of these two residues that are located in the C-terminal region plays a critical role in determining halophilic characteristics. The importance of these two residues versus the net negative charges will be discussed in relation to the halophilicity of NDK.
Figures

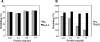


Similar articles
-
Surface acidic amino acid of Pseudomonas/Halomonas chimeric nucleoside diphosphate kinase leads effective recovery from heat-denaturation.Protein Pept Lett. 2013 Jul 1;20(7):836-41. doi: 10.2174/0929866511320070015. Protein Pept Lett. 2013. PMID: 22973841
-
Dimeric structure of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from moderately halophilic bacterium: contrast to the tetrameric Pseudomonas counterpart.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Mar;268(1):52-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00626.x. Epub 2007 Jan 15. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17227453
-
Residue 134 determines the dimer-tetramer assembly of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from moderately halophilic bacteria.FEBS Lett. 2008 Apr 2;582(7):1049-54. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.02.054. Epub 2008 Mar 3. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 18319059
-
[Halophilic enzymes: negative charges determine halophilicity].Seikagaku. 2009 May;81(5):401-6. Seikagaku. 2009. PMID: 19522299 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
[Molecular mechanism of halophilic enzyme-- nucleoside diphosphate kinase from extreme holophile].Seikagaku. 2009 Dec;81(12):1080-6. Seikagaku. 2009. PMID: 20077851 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional insights into thermally stable cytochrome c' from a thermophile.Protein Sci. 2017 Apr;26(4):737-748. doi: 10.1002/pro.3120. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28097774 Free PMC article.
-
Protein attributes contribute to halo-stability, bioinformatics approach.Saline Syst. 2011 May 18;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1746-1448-7-1. Saline Syst. 2011. PMID: 21592393 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel cold‑adapted GDSL family esterase from Photobacterium sp. strain J15.Extremophiles. 2016 Jan;20(1):44-55. doi: 10.1007/s00792-015-0796-4. Extremophiles. 2016. PMID: 26475626
-
Rational engineering of a mesohalophilic carbonic anhydrase to an extreme halotolerant biocatalyst.Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 21;6:10278. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10278. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26687908 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mercuric reductase from the unique deep brine environment of Atlantis II in the Red Sea.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1675-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.493429. Epub 2013 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24280218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal, R.P., Parks R.E., Jr Erythrocytic nucleoside diphosphokinase. V. Some properties and behavior of the pI 7.3 isozyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1971;246:2258–2264. - PubMed
-
- Dym, O., Mevarech, M., Sussman, J.L. Structure features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from an archaebacterium. Science. 1995;267:1344–1346. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg, H., Mevarech, M., Zaccai, G. Biochemical, structural, and molecular genetic aspects of halophilism. Adv. Protein Chem. 1992;43:1–62. - PubMed
-
- Frolow, F., Harel, M., Sussman, J.L., Mevarech, M., Shoham, M. Insights into protein adaptation to a saturated salt environment from the crystal structure of a halophilic 2Fe–2S ferredoxin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996;3:452–458. - PubMed
-
- Ishibashi, M., Tokunaga, H., Hiratsuka, K., Yonezawa, Y., Turumaru, H., Arakawa, T., Tokunaga, M. NaCl-activated nucleoside diphosphate kinase from extremely halophilic archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum, maintain native conformation without salt. FEBS Lett. 2001;493:134–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

