STAP-2 negatively regulates both canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus-derived latent membrane protein 1
- PMID: 18573890
- PMCID: PMC2519705
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00194-08
STAP-2 negatively regulates both canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus-derived latent membrane protein 1
Abstract
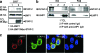
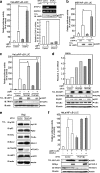
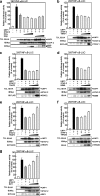
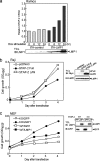
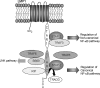
The signal-transducing adaptor protein 2 (STAP-2) is a recently identified adaptor protein that contains a pleckstrin homology (PH) and Src homology 2 (SH2)-like domains, as well as a proline-rich domain in its C-terminal region. In previous studies, we demonstrated that STAP-2 binds to MyD88 and IKK-alpha or IKK-beta and modulates NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages. In the present study, we found that ectopic expression of STAP-2 inhibited Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling and interleukin-6 expression. Indeed, STAP-2 associated with LMP1 through its PH and SH2-like domains, and these proteins interacted with each other in EBV-positive human B cells. We found, furthermore, that STAP-2 regulated LMP1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling through direct or indirect interactions with the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and TNFR-associated death domain (TRADD) proteins. STAP-2 mRNA was induced by the expression of LMP1 in human B cells. Furthermore, transient expression of STAP-2 in EBV-positive human B cells decreased cell growth. Finally, STAP-2 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts showed enhanced LMP1-induced cell growth. These results suggest that STAP-2 acts as an endogenous negative regulator of EBV LMP1-mediated signaling through TRAF3 and TRADD.
Figures
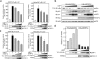

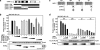



Similar articles
-
The C-terminal activating region 2 of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates NF-kappaB through TRAF6 and TAK1.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 27;281(4):2162-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505903200. Epub 2005 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16280329
-
BS69 negatively regulates the canonical NF-kappaB activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus-derived LMP1.FEBS Lett. 2009 May 19;583(10):1567-74. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.04.022. Epub 2009 Apr 18. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19379743
-
BS69 cooperates with TRAF3 in the regulation of Epstein-Barr virus-derived LMP1/CTAR1-induced NF-kappaB activation.FEBS Lett. 2010 Mar 5;584(5):865-72. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.060. Epub 2010 Feb 5. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20138174
-
Adaptor protein STAP-2 modulates cellular signaling in immune systems.Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(2):185-94. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b13-00421. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014. PMID: 24492713 Review.
-
[Novel adaptor protein, STAP-2 functions as a signal modulator in immune system].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Jun;130(6):769-75. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.769. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20519854 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The A20 deubiquitinase activity negatively regulates LMP1 activation of IRF7.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(12):6130-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00364-10. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20392859 Free PMC article.
-
The human transcriptome during nontyphoid Salmonella and HIV coinfection reveals attenuated NFkappaB-mediated inflammation and persistent cell cycle disruption.J Infect Dis. 2011 Oct 15;204(8):1237-45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir512. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21917897 Free PMC article.
-
Zipper-interacting protein kinase (ZIPK) modulates canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through interaction with Nemo-like kinase and T-cell factor 4 (NLK/TCF4).J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):19170-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.189829. Epub 2011 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454679 Free PMC article.
-
STAP-1-derived peptide suppresses TCR-mediated T cell activation and ameliorates immune diseases by inhibiting STAP-1-LCK binding.Immunohorizons. 2025 Apr 26;9(6):vlaf015. doi: 10.1093/immhor/vlaf015. Immunohorizons. 2025. PMID: 40288812 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of targeting signal-transducing adaptor protein-2 in cancer therapeutic applications.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(2):251-259. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00216. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 38745775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brinkmann, M. M., and T. F. Schulz. 2006. Regulation of intracellular signalling by the terminal membrane proteins of members of the Gammaherpesvirinae. J. Gen. Virol. 871047-1074. - PubMed
-
- Brodeur, S. R., G. Cheng, D. Baltimore, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1997. Localization of the major NF-kappaB-activating site and the sole TRAF3 binding site of LMP-1 defines two distinct signaling motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 27219777-19784. - PubMed
-
- Busch, L. K., and G. A. Bishop. 2001. Multiple carboxyl-terminal regions of the EBV oncoprotein, latent membrane protein 1, cooperatively regulate signaling to B lymphocytes via TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-dependent and TRAF-independent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 1675805-5813. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary, P. M., A. Jasmin, M. T. Eby, and L. Hood. 1999. Modulation of the NF-kappa B pathway by virally encoded death effector domains-containing proteins. Oncogene 185738-5746. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, G., and D. Baltimore. 1996. TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF and CD40L-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Genes Dev. 10963-973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
