Comparison of the susceptibilities of C57BL/6 and A/J mouse strains to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection
- PMID: 18573893
- PMCID: PMC2519407
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00350-08
Comparison of the susceptibilities of C57BL/6 and A/J mouse strains to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection
Abstract
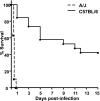
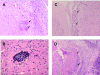
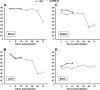
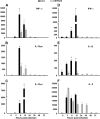
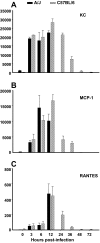
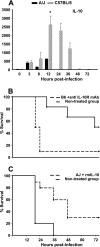
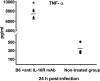
Streptococcus suis is an important swine and human pathogen. Assessment of susceptibility to S. suis using animal models has been limited to monitoring mortality rates. We recently developed a hematogenous model of S. suis infection in adult CD1 outbred mice to study the in vivo development of an early septic shock-like syndrome that leads to death and a late phase that clearly induces central nervous system damage, including meningitis. In the present study, we compared the severities of septic shock-like syndrome caused by S. suis between adult C57BL/6J (B6) and A/J inbred mice. Clinical parameters, proinflammatory mediators, and bacterial clearance were measured to dissect potential immune factors associated with genetic susceptibility to S. suis infection. Results showed that A/J mice were significantly more susceptible than B6 mice to S. suis infection, especially during the acute septic phase of infection (100% of A/J and 16% of B6 mice died before 24 h postinfection). The greater susceptibility of A/J mice was associated with an exaggerated inflammatory response, as indicated by their higher production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-12p40/p70 (IL-12p40/p70), gamma interferon, and IL-1beta, but not with different bacterial loads in the blood. In addition, IL-10 was shown to be responsible, at least in part, for the higher survival in B6 mice. Our findings demonstrate that A/J mice are very susceptible to S. suis infection and provide evidence that the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators is crucial for host survival during the septic phase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting TREM-1 Signaling in the Presence of Antibiotics is Effective Against Streptococcal Toxic-Shock-Like Syndrome (STSLS) Caused by Streptococcus suis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Nov 12;5:79. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00079. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26618144 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2-independent host innate immune response against an epidemic strain of Streptococcus suis that causes a toxic shock-like syndrome in humans.PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e65031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065031. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724118 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis serotype 2, an important swine and human pathogen, induces strong systemic and cerebral inflammatory responses in a mouse model of infection.J Immunol. 2007 Aug 1;179(3):1842-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1842. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17641051
-
Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis.Future Microbiol. 2012 Feb;7(2):259-79. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.149. Future Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22324994 Review.
-
Streptococcus suis vaccines: candidate antigens and progress.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14(12):1587-608. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1101349. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 26468755 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of candidate susceptibility and resistance genes of mice infected with Streptococcus suis type 2.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032150. Epub 2012 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384161 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic, microbial and environmental standardization in animal experimentation limiting immunological discovery.BMC Immunol. 2020 Sep 2;21(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12865-020-00380-x. BMC Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32878597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catabolite control protein A of Streptococcus suis type 2 contributes to sugar metabolism and virulence.J Microbiol. 2012 Dec;50(6):994-1002. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-2035-3. Epub 2012 Dec 30. J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23274986
-
Baicalein Ameliorates Streptococcus suis-Induced Infection In Vitro and In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 29;22(11):5829. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115829. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072443 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Analysis of PRRSV-Infected Porcine Dendritic Cell Response to Streptococcus suis Infection Reveals Up-Regulation of Inflammatory-Related Genes Expression.PLoS One. 2016 May 23;11(5):e0156019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156019. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27213692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arends, J. P., and H. C. Zanen. 1988. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev. Infect. Dis. 10131-137. - PubMed
-
- Bahloul, H., A. Mofredj, A. Mrabet, G. Gineyt, and P. Rousselier. 2008. Streptococcus suis meningitis after oral contamination? Med. Mal. Infect. 38281-282. - PubMed
-
- Beaudoin, M., R. Higgins, J. Harel, and M. Gottschalk. 1992. Studies on a murine model for evaluation of virulence of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 isolates. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 99111-116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

