Subtle neurological abnormalities as risk factors for cognitive and functional decline, cerebrovascular events, and mortality in older community-dwelling adults
- PMID: 18574083
- PMCID: PMC4642714
- DOI: 10.1001/archinte.168.12.1270
Subtle neurological abnormalities as risk factors for cognitive and functional decline, cerebrovascular events, and mortality in older community-dwelling adults
Abstract
Background: Subtle, but clinically detectable, neurological abnormalities (SNAs) are associated with impaired physical performance in elderly persons without overt neurological diseases. We investigated whether SNAs were prospectively associated with cognitive and functional status, death, and cerebrovascular events (CVEs) in older community-dwelling individuals.
Methods: In participants without history of stroke, parkinsonism and dementia, or cognitive impairment, a score (N(SNA)) was obtained by summing SNAs detected with a simple neurological examination. Cognitive status and disability were reassessed 4 years later, and deaths and CVEs were documented over 8 years.
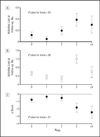
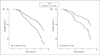
Results: Of 506 participants free of neurological diseases (mean [SEM] age, 71.9 [0.3] years; 42% were men), 59% had an N(SNA) of 1 or more (mean [SEM], 1.1 [0.06]; range, 0-8). At baseline, the N(SNA) increased with age and with declining cognitive and physical performance, depressive symptoms, and disability, after adjusting for several covariates, but did not increase with falls and urinary incontinence. The N(SNA) prospectively predicted worsening cognitive status and disability, adjusting for demographics and for baseline comorbidity and cognitive and physical performance. The mortality rates were 22.6, 23.3, 23.9, 58.6, and 91.9 per 1000 person-years in participants with an N(SNA) of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 or higher, respectively. Compared with an N(SNA) of less than 3, having an N(SNA) of 3 or higher was associated with an increased adjusted risk of death (hazard ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.25-2.74) and of CVE (hazard ratio, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.07-3.54) over 8 years.
Conclusion: In this sample of older community-dwelling persons without overt neurological diseases, multiple SNAs were associated with cognitive and functional decline and independently predicted mortality and CVEs.
Figures
Comment in
-
Subtle neurological abnormalities and functional cognition in older adults.Arch Intern Med. 2008 Jun 23;168(12):1252-3. doi: 10.1001/archinte.168.12.1252. Arch Intern Med. 2008. PMID: 18574079 No abstract available.
References
-
- Enright PL, McBurnie MA, Bittner V, et al. The 6-min walk test: a quick measure of functional status in elderly adults. Chest. 2003;123(2):387–398. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Haggerty CL, Kritchevsky SB, Nevitt MC, Simonsick EM. Walking performance and cardiovascular response: associations with age and morbidity: the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58(8):715–720. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Gottdiener JS, Mcburnie MA, et al. Associations of subclinical cardiovascular disease with frailty. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M158–M166. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Arnold AM, Naydeck BL, et al. “Successful aging”: effect of subclinical cardiovascular disease. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(19):2315–2322. - PubMed
-
- Rosano C, Kuller LH, Chung H, Arnold AM, Longstreth WT, Jr, Newman AB. Subclinical brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities predict physical functional decline in high-functioning older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(4):649–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

