Topoisomerase levels determine chemotherapy response in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 18574145
- PMCID: PMC2435590
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803513105
Topoisomerase levels determine chemotherapy response in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
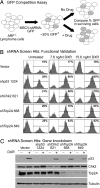
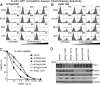
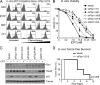
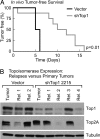
Topoisomerase poisons are chemotherapeutic agents that are used extensively for treating human malignancies. These drugs can be highly effective, yet tumors are frequently refractory to treatment or become resistant upon tumor relapse. Using a pool-based RNAi screening approach and a well characterized mouse model of lymphoma, we explored the genetic basis for heterogeneous responses to topoisomerase poisons in vitro and in vivo. These experiments identified Top2A expression levels as major determinants of response to the topoisomerase 2 poison doxorubicin and showed that suppression of Top2A produces resistance to doxorubicin in vitro and in vivo. Analogously, using a targeted RNAi approach, we demonstrated that suppression of Top1 produces resistance to the topoisomerase 1 poison camptothecin yet hypersensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin. Importantly, lymphomas relapsing after treatment display spontaneous changes in topoisomerase levels as predicted by in vitro gene knockdown studies. These results highlight the utility of pooled shRNA screens for identifying genetic determinants of chemotherapy response and suggest strategies for improving the effectiveness of topoisomerase poisons in the clinic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
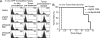
References
-
- Gros P, Ben Neriah YB, Croop JM, Housman DE. Isolation and expression of a complementary DNA that confers multidrug resistance. Nature. 1986;323:728–731. - PubMed
-
- Mao Y, et al. Mutations of human topoisomerase IIα affecting multidrug resistance and sensitivity. Biochemistry. 1999;38:10793–10800. - PubMed
-
- Shah NP, et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993;74:957–967. - PubMed
-
- Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

