Central sleep apnea: implications for congestive heart failure
- PMID: 18574295
- PMCID: PMC2774238
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.07-0871
Central sleep apnea: implications for congestive heart failure
Abstract
Congestive heart failure (HF), an exceedingly common and costly disease, is frequently seen in association with central sleep apnea (CSA), which often manifests as a periodic breathing rhythm referred to as Cheyne-Stokes respiration. CSA has historically been considered to be a marker of heart disease, since improvement in cardiac status is often associated with the attenuation of CSA. However, this mirroring of HF and CSA may suggest bidirectional importance to their relationship. In fact, observational data suggest that CSA, associated with repetitive oxyhemoglobin desaturations and surges in sympathetic neural activity, may be of pathophysiologic significance in HF outcomes. In light of the disappointing results from the first large trial assessing therapy with continuous positive airway pressure in patients with CSA and HF, further large-scale interventional trials will be needed to assess the role, if any, of CSA treatment on the outcomes of patients with HF. This review will discuss epidemiologic, pathophysiologic, diagnostic, and therapeutic considerations of CSA in the setting of HF.
Figures
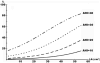
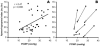
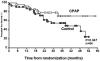

References
-
- Javaheri S, Parker TJ, Liming JD, et al. Sleep apnea in 81 ambulatory male patients with stable heart failure: types and their prevalences, consequences, and presentations. Circulation. 1998;97:2154–2159. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2002;106:3068–3072. - PubMed
-
- Sin DD, Fitzgerald F, Parker JD, et al. Risk factors for central and obstructive sleep apnea in 450 men and women with congestive heart failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:1101–1106. - PubMed
-
- Badr MS, Toiber F, Skatrud JB, et al. Pharyngeal narrowing/occlusion during central sleep apnea. J Appl Physiol. 1995;78:1806–1815. - PubMed
-
- Tkacova R, Niroumand M, Lorenzi-Filho G, et al. Overnight shift from obstructive to central apneas in patients with heart failure: role of Pco2 and circulatory delay. Circulation. 2001;103:238–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

