Association of HMGB1 polymorphisms with outcome in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- PMID: 18577209
- PMCID: PMC2481482
- DOI: 10.1186/cc6935
Association of HMGB1 polymorphisms with outcome in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: High mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) is a pleiotropic cytokine, recently implicated in the pathophysiology of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis. Data from experimental sepsis models show that administration of anti-HMGB1 antibodies significantly decreased mortality, even when administration was delayed for 24 hours, providing a window of opportunity for therapeutic intervention if transferred into a clinical setting. Whether genetic variation in the human HMGB1 gene is associated with disease susceptibility is unknown.
Methods: We sequenced the HMGB1 gene in 239 prospectively monitored patients with SIRS admitted to an intensive care unit and we measured the corresponding HMGB1 serum concentrations. Blood donors served as control individuals. Outcome parameters according to different HMGB1 genotypes were compared.
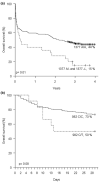
Results: Homozygosity and heterozygosity for a promoter variant (-1377delA) was associated with a decreased overall 4-year survival (15% versus 44%, hazard ratio = 1.80; P = 0.01) and with a decreased number of SIRS criteria. Carriage of an exon 4 variant (982C>T) was significantly associated with an increased number of SIRS criteria, a higher Simplified Acute Physiology Score II score, a lower PaO2/FiO2 ratio and lower serum HMGB1 levels (P = 0.01), and with a significantly higher probability of early death due to infection (P = 0.04). HMGB1 was undetectable in the control individuals.
Conclusion: The present article is the first report of clinical implications of variation in the human HMGB1 gene. Two polymorphisms were determined as significant risk factors associated with early and late mortality, which may provide insight into the molecular background of SIRS and sepsis, suggesting a possible role for HMGB1 genetics in future prognostic evaluation.
Figures

Comment in
-
High mobility group box-1 protein--one step closer to the clinic?Crit Care. 2008;12(4):168. doi: 10.1186/cc6944. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 18671827 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Association of HMGB1 polymorphisms with outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010 Feb;16(2):239-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.10.002. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19819342
-
Impact of serum high-mobility group box 1 protein elevation on oxygenation impairment after thoracic aortic aneurysm repair.Heart Vessels. 2011 May;26(3):306-12. doi: 10.1007/s00380-010-0056-6. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Heart Vessels. 2011. PMID: 21052685
-
High-mobility group box 1 as a surrogate prognostic marker in dogs with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2010 Jun;20(3):298-302. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-4431.2010.00539.x. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2010. PMID: 20636982
-
[Inflammation and its regulatory system].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Dec;62(12):2229-35. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15597789 Review. Japanese.
-
Targeting HMGB1 in the treatment of sepsis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Mar;18(3):257-68. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.863876. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24392842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of high-mobility group box 1 with susceptibility and clinicopathological characteristics of uterine cervical neoplasia in Taiwanese women.Tumour Biol. 2016 Dec;37:15813–15823. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5408-0. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27704361
-
Associations between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of High Mobility Group Box 1 Protein and Clinical Outcomes in Korean Sepsis Patients.Yonsei Med J. 2016 Jan;57(1):111-7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.111. Yonsei Med J. 2016. PMID: 26632390 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic HMGB1 Mediates Autophagy Activation in an Emulsified Isoflurane Anesthesia Cell Model.Neurochem Res. 2019 May;44(5):1090-1100. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02740-5. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30712242
-
Chrysophanol alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic db/db mice by regulating the SIRT1/HMGB1/NF-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4406-4412. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8083. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31772635 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 in health and disease.Mol Aspects Med. 2014 Dec;40:1-116. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Mol Aspects Med. 2014. PMID: 25010388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

