Factitious lymphoedema as a psychiatric condition mimicking reflex sympathetic dystrophy: a case report
- PMID: 18577230
- PMCID: PMC2474643
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-2-216
Factitious lymphoedema as a psychiatric condition mimicking reflex sympathetic dystrophy: a case report
Abstract
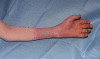
Introduction: Reflex sympathetic dystrophy can result in severe disability with only one in five patients able to fully resume prior activities. Therefore, it is important to diagnose this condition early and begin appropriate treatment. Factitious lymphoedema can mimic reflex sympathetic dystrophy and is caused by self-inflicted tourniquets, blows to the arm or repeated skin irritation. Patients with factitious lymphoedema have an underlying psychiatric disorder but usually present to emergency or orthopaedics departments. Factitious lymphoedema can then be misdiagnosed as reflex sympathetic dystrophy. The treatment for factitious lymphoedema is dealing with the underlying psychiatric condition.
Case presentation: We share our experience of treating a 33-year-old man, who presented with factitious lymphoedema, initially diagnosed as reflex sympathetic dystrophy.
Conclusion: Awareness of this very similar differential diagnosis allows early appropriate treatment to be administered.
Figures
References
-
- Subbarao J, Stillwell G. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome of the upper extremity: analysis of total outcome of management of 125 cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1981;62:B549–B554. - PubMed
-
- Atkins R, Duckworth T, Kanis J. Features of algodystrophy after Colles fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Louis D, Lamp M, Greene T. The upper extremity and psychiatric illness. J Hand Surg Am. 1985;10:687–693. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources