The role of retinoblastoma-associated proteins 46 and 48 in estrogen receptor alpha mediated gene expression
- PMID: 18577416
- PMCID: PMC2642675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.05.016
The role of retinoblastoma-associated proteins 46 and 48 in estrogen receptor alpha mediated gene expression
Abstract
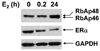
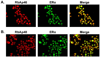
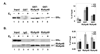
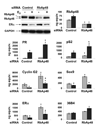
The differential recruitment of coregulatory proteins to the DNA-bound estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) plays a critical role in mediating estrogen-responsive gene expression. We previously isolated and identified retinoblastoma-associated proteins 46 (RbAp46) and 48 (RbAp48), which are associated with chromatin remodeling, histone deacetylation, and transcription repression, as proteins associated with the DNA-bound ERalpha. We now demonstrate that RbAp46 and RbAp48 interact with ERalphain vitro and in vivo, associate with ERalpha at endogenous, estrogen-responsive genes, and alter expression of endogenous, ERalpha-activated and -repressed genes in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Our findings reveal that RbAp48 limits expression of estrogen-responsive genes and that RbAp46 modulates estrogen responsiveness in a gene-specific manner. The ability of RbAp46 and RbAp48 to interact with ERalpha and influence its activity reveals yet another role for these multifunctional proteins in regulating gene expression.
Figures

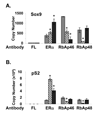
References
-
- Ahringer J. NuRD and SIN3 histone deacetylase complexes in development. Trends Genet. 2000;16:351–356. - PubMed
-
- Bowen NJ, Fujita N, Kajita M, Wade PA. Mi-2/NuRD: multiple complexes for many purposes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1677:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Carroll J, Meyer C, Song J, Li W, Geistlinger T, Eeckhoute J, Brodshy A, Keeton E, Fertuck K, Hall G, Wang Q, Bekiranov S, Sementchenko V, Fox E, Silver P, Gingeras T, Liu X, Brown M. Genome-wide analysis of estrogen receptor binding sites. Nat Genetics. 2006;38:1289–1297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

