Rap1 activation plays a regulatory role in pancreatic amylase secretion
- PMID: 18577515
- PMCID: PMC2527106
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M800754200
Rap1 activation plays a regulatory role in pancreatic amylase secretion
Abstract
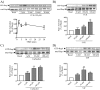
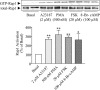
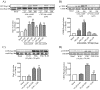
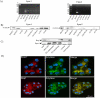
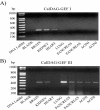
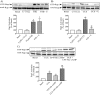
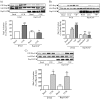
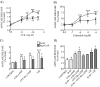
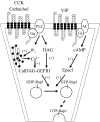
Rap1 is a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins and is localized on pancreatic zymogen granules. The current study was designed to determine whether GTP-Rap1 is involved in the regulation of amylase secretion. Rap1A/B and the two Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factors, Epac1 and CalDAG-GEF III, were identified in mouse pancreatic acini. A fraction of both Rap1 and Epac1 colocalized with amylase in zymogen granules, but only Rap1 was integral to the zymogen granule membranes. Stimulation with cholecystokinin (CCK), carbachol, and vasoactive intestinal peptide all induced Rap1 activation, as did calcium ionophore A23187, phorbol ester, forskolin, 8-bromo-cyclic AMP, and the Epac-specific cAMP analog 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP. The phospholipase C inhibitor U-73122 abolished carbachol- but not forskolin-induced Rap1 activation. Co-stimulation with carbachol and 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP led to an additive effect on Rap1 activation, whereas a synergistic effect was seen on amylase release. Although the protein kinase A inhibitor H-89 abolished forskolin-stimulated CREB phosphorylation, it did not modify forskolin-induced GTP-Rap1 levels, excluding PKA participation. Overexpression of Rap1 GTPase-activating protein, which blocked Rap1 activation, reduced the effect of 8-bromo-cyclic AMP, 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP, and vasoactive intestinal peptide on amylase release by 60% and reduced CCK- as well as carbachol-stimulated pancreatic amylase release by 40%. These findings indicate that GTP-Rap1 is required for pancreatic amylase release. Rap1 activation not only mediates the cAMP-evoked response via Epac1 but is also involved in CCK- and carbachol-induced amylase release, with their action most likely mediated by CalDAG-GEF III.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Rap1 activation and insulin secretagogue properties of an acetoxymethyl ester of an Epac-selective cyclic AMP analog in rat INS-1 cells: studies with 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP-AM.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10728-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900166200. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19244230 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate regulation of forskolin-induced cellular proliferation in macrophages by protein kinase A/cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) and Epac1-Rap1 signaling: effects of silencing CREB gene expression on Akt activation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 18;280(46):38276-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507332200. Epub 2005 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16172130
-
PKA and Epac cooperate to augment bradykinin-induced interleukin-8 release from human airway smooth muscle cells.Respir Res. 2009 Sep 29;10(1):88. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-88. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19788733 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between cAMP signalling and sulfonylurea in insulin secretion.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Sep;16 Suppl 1:118-25. doi: 10.1111/dom.12343. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 25200305 Review.
-
Regulatory actions of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on osteoclast function: possible roles of Epac-mediated signaling.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Dec;1433(1):18-28. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13861. Epub 2018 May 30. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 29846007 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular architecture of mouse and human pancreatic zymogen granules: protein components and their copy numbers.Biophys Rep. 2018;4(2):94-103. doi: 10.1007/s41048-018-0055-1. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Biophys Rep. 2018. PMID: 29756009 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor mediates a switch in intracellular signaling for PGE2-induced sensitization of sensory neurons from protein kinase A to Epac.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 15;9(8):e104529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104529. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25126967 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized amplification and single-cell analysis identify GnRH-mediated activation of Rap1b in primary rat gonadotropes.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Mar 5;350(1):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.11.017. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22127306 Free PMC article.
-
Small G proteins as key regulators of pancreatic digestive enzyme secretion.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Mar;296(3):E405-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90874.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19088252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Epac1 is required for cAMP-mediated invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017 Jan;211:67-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 27984073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bos, J. L. (2005) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17 123-128 - PubMed
-
- Yamashita, S., Mochizuki, N., Ohba, Y., Tobiume, M., Okada, Y., Sawa, H., Nagashima, K., and Matsuda, M. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 25488-25493 - PubMed
-
- de Rooij, J., Zwartkruis, F. J., Verheijen, M. H., Cool, R. H., Nijman, S. M., Wittinghofer, A., and Bos, J. L. (1998) Nature 396 474-477 - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki, H., Springett, G. M., Mochizuki, N., Toki, S., Nakaya, M., Matsuda, M., Housman, D. E., and Graybiel, A. M. (1998) Science 282 2275-2279 - PubMed
-
- Quilliam, L. A., Mueller, H., Bohl, B. P., Prossnitz, V., Sklar, L. A., Der, C. J., and Bokoch, G. M. (1991) J. Immunol. 147 1628-1635 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

