Measurement of pulsatile insulin secretion in the rat: direct sampling from the hepatic portal vein
- PMID: 18577690
- PMCID: PMC2536733
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90335.2008
Measurement of pulsatile insulin secretion in the rat: direct sampling from the hepatic portal vein
Abstract
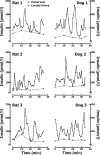
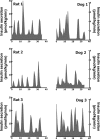
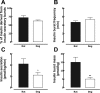
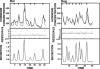
It has previously been shown that insulin is secreted in discrete secretory bursts by sampling directly from the portal vein in the dog and humans. Deficient pulsatile insulin secretion is the basis for impaired insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes. However, while novel genetically modified disease models of diabetes are being developed in rodents, no validated method for quantifying pulsatile insulin secretion has been established for rodents. To address this we 1) developed a novel rat model with chronically implanted portal vein catheters, 2) established the parameters to permit deconvolution of portal vein insulin concentrations profiles to measure insulin secretion and resolve its pulsatile components, and 3) measured total and pulsatile insulin secretion compared with that in the dog, the species in which this sampling and deconvolution approach was validated for quantifying pulsatile insulin secretion. In rats, portal vein catheter patency and function were maintained for periods up to 2-3 wk with no postoperative complications such as catheter tract infection. Rat portal vein insulin concentration profiles in the fasting state revealed distinct insulin oscillations with a periodicity of approximately 5 min and an amplitude of up to 600 pmol/l, which was remarkably similar to that in the dogs and in humans. Deconvolution analysis of portal vein insulin concentrations revealed that the majority of insulin ( approximately 70%) in the rat is secreted in distinct insulin pulses occurring at approximately 5-min intervals. This model therefore permits direct accurate measurements of pulsatile insulin secretion in a relatively inexpensive animal. With increased introduction of genetically modified rat models will be an important tool in elucidating the underlying mechanisms of impaired pulsatile insulin secretion in diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Akaike H An information criterion (AIC). Math Sci 14: 5–9, 1976.
-
- Basu R, Breda E, Oberg AL, Powell CC, Dalla Man C, Basu A, Vittone JL, Klee GG, Arora P, Jensen MD, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Rizza RA. Mechanisms of the age-associated deterioration in glucose tolerance: contribution of alterations in insulin secretion, action, and clearance. Diabetes 52: 1738–1748, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bertram R, Sherman A, Satin LS. Metabolic and electrical oscillations: partners in controlling pulsatile insulin secretion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E890–E900, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bonora E, Zavaroni I, Coscelli C, Butturini U. Decreased hepatic insulin extraction in subjects with mild glucose intolerance. Metabolism 32: 438–446, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Bratusch-Marrain PR, Komjati M, Waldhausl WK. Efficacy of pulsatile vs. continuous insulin administration on hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization in type I diabetic humans. Diabetes 35: 922–926, 1986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

