Double oxygen-sensing vector system for robust hypoxia/ischemia-regulated gene induction in cardiac muscle in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 18578010
- PMCID: PMC2716210
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2008.136
Double oxygen-sensing vector system for robust hypoxia/ischemia-regulated gene induction in cardiac muscle in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
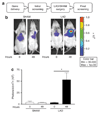
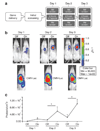
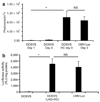
High-fidelity genetically encoded bio-sensors that respond to changes in cellular environmental milieu in disease offer great potential in a range of patho-physiological settings. Here a unique hypoxia-regulated vector-based system with double oxygen-sensing transcriptional elements was developed for rapid and robust hypoxia-regulated gene expression in the heart. Hypoxia-responsive cis elements were used in tandem with a single proline-modified oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domain of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha to form a double oxygen-sensing vector system (DOSVS). In adult cardiac myocytes in vitro, the DOSVS demonstrated a low background expression not different from baseline control in normoxia, and with 100% efficiency, robust, 1,000-fold induction upon hypoxia. In the heart in vivo, hypoxic and ischemic challenges elicited rapid 700-fold induction in living animals, exceeding that obtained by a high-fidelity constitutive cytomegalovirus (CMV) viral promoter. DOSVS also showed high temporal resolution in the heart in response to cyclical bouts of hypoxia in vivo. We propose that DOSVS will be valuable for a range of applications, including bio-sensing and therapeutic gene expression in the heart and other organ systems that are confronted by chronic or episodic hypoxic/ischemic stresses in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Yenari MA, Sapolsky RM. Gene therapy in neurological disease. Methods Mol Med. 2005;104:75–88. - PubMed
-
- Woo SL, Skarlatos SI, Joyce MM, Croxton TL, Qasba P. Critical resources for gene therapy in Heart, Lung, and Blood Diseases Working Group. Mol Ther. 2006;13:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Williams ML, Koch WJ. Viral-based myocardial gene therapy approaches to alter cardiac function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2004;66:49–75. - PubMed
-
- Pachori AS, Melo LG, Dzau VJ. Gene therapy: role in myocardial protection. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006:335–350. - PubMed
-
- Hermonat PL, Mehta JL. Potential of gene therapy for myocardial ischemia. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004;19:517–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

