Amazing stability of phosphate-quaternary amine interactions
- PMID: 18578519
- PMCID: PMC2556961
- DOI: 10.1021/pr8001595
Amazing stability of phosphate-quaternary amine interactions
Abstract
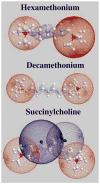
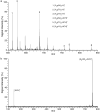
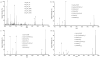
We have previously used MALDI mass spectrometry to highlight ammonium- or guanidinium-aromatic interactions via cation-pi bonding and ammonium- or guanidinium-phosphate interactions through salt bridge formation. In the present work, the gas-phase stability and dissociation pathways of the interaction between phosphorylated peptides and compounds containing quaternary amines are demonstrated using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. The presence of one quaternary amine in a compound is enough to form a noncovalent complex with a phosphorylated residue. However, if two quaternary amines are present in one molecule, the electrostatic interactions of the quaternary amines with the phosphate results in a "covalent-like" stability, and these bonds can withstand fragmentation by collision-induced dissociation at energies similar to those that fragment covalent bonds. Such interactions are important in accounting for physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological effects of many therapeutic compounds and small molecules containing quaternary amines or phosphates.
Figures
References
-
- Woods AS. The Mighty Arginine, the Stable Quaternary Amines, the Powerful Aromatics and the Aggressive Phosphate: Their Role in the Noncovalent Minuet. J Proteome Res. 2004;3:478–484. - PubMed
-
- Woods AS, Moyer SC, Wang HY, Wise RA. Interaction of Chlorisondamine with the Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. J of Proteome Research. 2003;2:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Wang HYJ, Taggi AE, Meinwald J, Wise RA, Woods AS. A Study of the Interaction of Chlorisondamine and Chlorisondamine analogs with An Epitope of the α−2 Neuronal Acetylcholine Nicotinic Receptor Subunit. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:532–539. - PubMed
-
- Johnson LN, Lewis RJ. Structural basis for control by phosphorylation. Chem Rev. 2001;101:2209–2242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

