Proteomic analysis of the balance between survival and cell death responses in cisplatin-mediated ototoxicity
- PMID: 18578524
- PMCID: PMC2570323
- DOI: 10.1021/pr8002479
Proteomic analysis of the balance between survival and cell death responses in cisplatin-mediated ototoxicity
Abstract
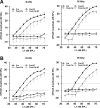
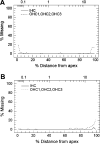
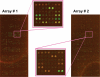
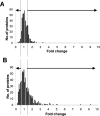
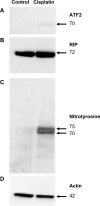
Cisplatin, a widely used anticancer drug, preferentially damages outer hair cells (OHCs) of the inner ear. In this study, an antibody microarray was used to identify early changes in protein expression in the rat cochlea induced by cisplatin. Only small changes in hearing thresholds (4-34 dB elevation) were detected two days after cisplatin treatment (12 mg/kg). OHC function, measured by otoacoustic emissions, was slightly depressed (10 dB), and little or no receptor cell loss was observed. However, cisplatin induced large changes in the expression of 19 proteins involved in apoptosis, cell survival, or progression through the cell cycle. Fifteen of the proteins are novel to the study of the inner ear. Immunoblotting confirmed increases in the levels of the pro-survival activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2), of pro-apoptotic serine-threonine protein kinase, receptor interacting protein, and a 70/75 kDa nitrotyrosine bearing doublet of unknown function. Anti-nitrotyrosine antibodies localized these oxidatively damaged proteins to the stereocilia of OHCs, the Golgi-centrosome region of Hensen's cells, nuclei of outer pillar cells, and tunnel crossing fibers innervating OHCs. The results of this proteomic analysis reflect the commencement of ototoxic and cell survival responses before the observation of a significant functional or anatomical loss.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Necroptosis and Apoptosis Contribute to Cisplatin and Aminoglycoside Ototoxicity.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 10;39(15):2951-2964. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1384-18.2019. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30733218 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein is not dependent on caspase inhibition.Otol Neurotol. 2007 Apr;28(3):417-25. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000247826.28893.7a. Otol Neurotol. 2007. PMID: 17211286
-
Evaluating protective and therapeutic effects of alpha-lipoic acid on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Aug 1;9(8):827. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0888-z. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30068942 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A1 Receptor Protects Against Cisplatin Ototoxicity by Suppressing the NOX3/STAT1 Inflammatory Pathway in the Cochlea.J Neurosci. 2016 Apr 6;36(14):3962-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3111-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27053204 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: From signaling network to therapeutic targets.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jan;157:114045. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114045. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36455457 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Analysis in Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: A Study in Wistar Rat.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0138027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138027. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26366995 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain-induced cochlear degeneration in rat.Neurotox Res. 2012 Aug;22(2):158-69. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9320-0. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 22476946 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to reduce the risk of platinum containing antineoplastic drug-induced ototoxicity.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2020 Oct;16(10):965-982. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2020.1806235. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32757852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy attenuates noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative stress.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 May 20;22(15):1308-24. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6004. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25694169 Free PMC article.
-
Early transcriptional response to aminoglycoside antibiotic suggests alternate pathways leading to apoptosis in sensory hair cells in the mouse inner ear.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 May 21;9:190. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00190. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26052268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Ruijven MW, de Groot JC, Klis SF, Smoorenburg GF. The cochlear targets of cisplatin: an electrophysiological and morphological time-sequence study. Hear. Res. 2005;205(1—2):241–8. - PubMed
-
- Berndtsson M, Hagg M, Panaretakis T, Havelka AM, Shoshan MC, Linder S. Acute apoptosis by cisplatin requires induction of reactive oxygen species but is not associated with damage to nuclear DNA. Int. J. Cancer. 2007;120(1):175–80. - PubMed
-
- Anniko M, Sobin A. Cisplatin: evaluation of its ototoxic potential. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1986;7(4):276–93. - PubMed
-
- Meech RP, Campbell KC, Hughes LP, Rybak LP. A semiquantitative analysis of the effects of cisplatin on the rat stria vascularis. Hear. Res. 1998;124(1—2):44–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

