Respiratory impedance measurements for assessment of lung mechanics: focus on asthma
- PMID: 18579455
- PMCID: PMC2637462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2008.04.015
Respiratory impedance measurements for assessment of lung mechanics: focus on asthma
Abstract
This review discusses the history and current state of the art of the forced oscillation technique (FOT) to measure respiratory impedance. We focus on how the FOT and its interaction with models have emerged as a powerful method to extract out not only clinically relevant information, but also to advance insight on the mechanisms and structures responsible for human lung diseases, especially asthma. We will first provide a short history of FOT for basic clinical assessment either directly from the data or in concert with lumped element models to extract out specific effective properties. We then spend several sections on the more exciting recent advances of FOT to probe the relative importance of tissue versus airway changes in disease, the impact of the disease on heterogeneous lung function, and the relative importance of small airways via synthesis of FOT with imaging. Most recently, the FOT approach has been able to directly probe airway caliber in humans and the distinct airway properties of asthmatics that seem to be required for airway hyperresponsiveness. We introduce and discuss the mechanism and clinical implications of this approach, which may be substantial for treatment assessment. Finally, we highlight important future directions for the FOT, particularly its use to probe specific lung components (e.g., isolated airways, isolated airway smooth muscle, etc.) and relate such data to the whole lung. The intent is to substantially advance an integrated understanding of structure-function relationships in the lung.
Figures





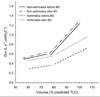
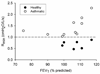

References
-
- Avanzolini G, Barbini P, Cappello A, Cevenini G. Real-time tracking of parameters of lung mechanics: emphasis on algorithm tuning. J. Biomed. Eng. 1990;12:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Bates JH, Lauzon AM, Dechman GS, Maksym GN, Schuessler TF. Temporal dynamics of pulmonary response to intravenous histamine in dogs: effects of dose and lung volume. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994;76:616–626. - PubMed
-
- Bates JH, Ludwig MS, Sly PD, Brown K, Martin JG, Fredberg JJ. Interrupter resistance elucidated by alveolar pressure measurement in open-chest normal dogs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988;65:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Bates JH, Lutchen KR. The interface between measurement and modeling of peripheral lung mechanics. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2005;148:153–164. - PubMed
-
- Black LD, Dellaca R, Jung K, Atileh H, Israel E, Ingenito EP, Lutchen KR. Tracking variations in airway caliber by using total respiratory vs. airway resistance in healthy and asthmatic subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003;95:511–518. - PubMed

