Loss of the N-linked glycan at residue 173 of human parainfluenza virus type 1 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase exposes a second receptor-binding site
- PMID: 18579600
- PMCID: PMC2519627
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00474-08
Loss of the N-linked glycan at residue 173 of human parainfluenza virus type 1 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase exposes a second receptor-binding site
Abstract
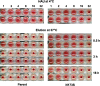
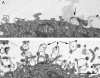
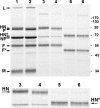
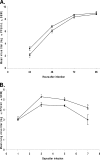
BCX 2798 (4-azido-5-isobutyrylamino-2,3-didehydro-2,3,4,5-tetradeoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosic acid) effectively inhibited the activities of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) of human parainfluenza viruses (hPIV) in vitro and protected mice from lethal infection with a recombinant Sendai virus whose HN was replaced with that of hPIV-1 (rSeV[hPIV-1HN]) (I. V. Alymova, G. Taylor, T. Takimoto, T. H. Lin., P. Chand, Y. S. Babu, C. Li, X. Xiong, and A. Portner, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:1495-1502, 2004). The ability of BCX 2798 to select drug-resistant variants in vivo was examined. A variant with an Asn-to-Ser mutation at residue 173 (N173S) in HN was recovered from mice after a second passage of rSeV(hPIV-1HN) in the presence of BCX 2798 (10 mg/kg of body weight daily). The N173S mutant remained sensitive to BCX 2798 in neuraminidase inhibition assays but was more than 10,000-fold less sensitive to the compound in hemagglutination inhibition tests than rSeV(hPIV-1HN). Its susceptibility to BCX 2798 in plaque reduction assays was reduced fivefold and did not differ from that of rSeV(hPIV-1HN) in mice. The N173S mutant failed to be efficiently eluted from erythrocytes and released from cells. It demonstrated reduced growth in cell culture and superior growth in mice. The results for gel electrophoresis analysis were consistent with the loss of the N-linked glycan at residue 173 in the mutant. Sequence and structural comparisons revealed that residue 173 on hPIV-1 HN is located close to the region of the second receptor-binding site identified in Newcastle disease virus HN. Our study suggests that the N-linked glycan at residue 173 masks a second receptor-binding site on hPIV-1 HN.
Figures
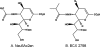
Similar articles
-
N-linked glycan at residue 523 of human parainfluenza virus type 3 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase masks a second receptor-binding site.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(6):3094-100. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02331-09. Epub 2010 Jan 6. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20053750 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation at residue 523 creates a second receptor binding site on human parainfluenza virus type 1 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein.J Virol. 2006 Sep;80(18):9009-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00969-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16940513 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the novel parainfluenza virus haemagglutinin-neuraminidase inhibitor BCX 2798 in mice - further evaluation.Antivir Ther. 2009;14(7):891-8. doi: 10.3851/IMP1420. Antivir Ther. 2009. PMID: 19918093 Free PMC article.
-
The hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoproteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 and Sendai virus have high structure-function similarity with limited antigenic cross-reactivity.Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):211-21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90201-2. Virology. 1990. PMID: 1689918
-
New antiviral approaches for human parainfluenza: Inhibiting the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase.Antiviral Res. 2019 Jul;167:89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 30951732 Review.
Cited by
-
Detailed genetic analysis of hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein gene in human parainfluenza virus type 1 isolates from patients with acute respiratory infection between 2002 and 2009 in Yamagata prefecture, Japan.Virol J. 2011 Dec 13;8:533. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-533. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 22152158 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-binding specificity of the human parainfluenza virus type 1 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein.Glycobiology. 2012 Feb;22(2):174-80. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwr112. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Glycobiology. 2012. PMID: 21846691 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hemagglutinin-neuraminidase inhibitors BCX 2798 and BCX 2855 on growth and pathogenicity of Sendai/human parainfluenza type 3 chimera virus in mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Sep;53(9):3942-51. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00220-09. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19564364 Free PMC article.
-
Addicted to sugar: roles of glycans in the order Mononegavirales.Glycobiology. 2019 Jan 1;29(1):2-21. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwy053. Glycobiology. 2019. PMID: 29878112 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling dynamics of paramyxovirus-receptor interactions using nanoparticles displaying hemagglutinin-neuraminidase.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 25;20(7):e1012371. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012371. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39052678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alymova, I. V., G. Taylor, T. Takimoto, T.-H. Lin, P. Chand, Y. S. Babu, C. Li, X. Xiong, and A. Portner. 2004. Efficacy of novel hemagglutinin-neuraminidase inhibitors BCX 2798 and BCX 2855 against human parainfluenza viruses in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 481495-1502. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alymova, I. V., A. Portner, T. Takimoto, K. L. Boyd, Y. S. Babu, and J. A. McCullers. 2005. The novel parainfluenza virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase inhibitor BCX 2798 prevents lethal synergism between a paramyxovirus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49398-405. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collier, A. M., and W. A. Clyde, Jr. 1977. Model systems for studying the pathogenesis of infections causing bronchiolitis in man. Pediatr. Res. 11243-246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

