Vectorial entry and release of hepatitis A virus in polarized human hepatocytes
- PMID: 18579610
- PMCID: PMC2519658
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00219-08
Vectorial entry and release of hepatitis A virus in polarized human hepatocytes
Abstract
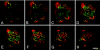
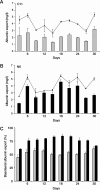
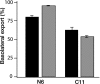
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is an enterically transmitted virus that replicates predominantly in hepatocytes within the liver before excretion via bile through feces. Hepatocytes are polarized epithelial cells, and it has been assumed that the virus load in bile results from direct export of HAV via the apical domain of polarized hepatocytes. We have developed a subclone of hepatocyte-derived HepG2 cells (clone N6) that maintains functional characteristics of polarized hepatocytes but displays morphology typical of columnar epithelial cells, rather than the complex morphology that is typical of hepatocytes. N6 cells form microcolonies of polarized cells when grown on glass and confluent monolayers of polarized cells on semipermeable membranes. When N6 microcolonies were exposed to HAV, infection was restricted to peripheral cells of polarized colonies, whereas all cells could be infected in colonies of nonpolarized HepG2 cells (clone C11) or following disruption of tight junctions in N6 colonies with EGTA. This suggests that viral entry occurs predominantly via the basolateral plasma membrane, consistent with uptake of virus from the bloodstream after enteric exposure, as expected. Viral export was also found to be markedly vectorial in N6 but not C11 cells. However, rather than being exported from the apical domain as expected, more than 95% of HAV was exported via the basolateral domain of N6 cells, suggesting that virus is first excreted from infected hepatocytes into the bloodstream rather than to the biliary tree. Enteric excretion of HAV may therefore rely on reuptake and transcytosis of progeny HAV across hepatocytes into the bile. These studies provide the first example of the interactions between viruses and polarized hepatocytes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biliary Secretion of Quasi-Enveloped Human Hepatitis A Virus.mBio. 2016 Dec 6;7(6):e01998-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01998-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27923925 Free PMC article.
-
Vectorial Release of Hepatitis E Virus in Polarized Human Hepatocytes.J Virol. 2019 Feb 5;93(4):e01207-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01207-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30463960 Free PMC article.
-
Specific IgA Enhances the Transcytosis and Excretion of Hepatitis A Virus.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 25;6:21855. doi: 10.1038/srep21855. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26911447 Free PMC article.
-
Quasi-enveloped hepatitis virus assembly and release.Adv Virus Res. 2020;108:315-336. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Adv Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 33837720 Review.
-
[Hepatitis A virus infection. A review].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2003 Oct 1;92(40):1659-73. doi: 10.1024/0369-8394.92.40.1659. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2003. PMID: 14579471 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Biliary Secretion of Quasi-Enveloped Human Hepatitis A Virus.mBio. 2016 Dec 6;7(6):e01998-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01998-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27923925 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Organoid Potential Application for Hepatitis E Virus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1417:133-139. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-1304-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37223863
-
Stem Cell-Derived Culture Models of Hepatitis E Virus Infection.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Mar 1;9(3):a031799. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031799. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 29686039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A research agenda for malaria eradication: basic science and enabling technologies.PLoS Med. 2011 Jan 25;8(1):e1000399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000399. PLoS Med. 2011. PMID: 21311584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SR-BI partner PDZK1 facilitates hepatitis C virus entry.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Oct 7;6(10):e1001130. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001130. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20949066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asher, L. V., L. N. Binn, T. L. Mensing, R. H. Marchwicki, R. A. Vassell, and G. D. Young. 1995. Pathogenesis of hepatitis A in orally inoculated owl monkeys (Aotus trivirgatus). J. Med. Virol. 47260-268. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, N. E., D. L. Hugo, S. V. Borovec, and D. A. Anderson. 1994. Rapid and efficient purification of hepatitis a virus from cell culture. J. Virol. Methods 47203-216. - PubMed
-
- Bomsel, M. 1997. Transcytosis of infectious human immunodeficiency virus across a tight human epithelial cell line barrier. Nat. Med. 342-47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

