Higher strength lanthanum carbonate provides serum phosphorus control with a low tablet burden and is preferred by patients and physicians: a multicenter study
- PMID: 18579668
- PMCID: PMC2518797
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.04741107
Higher strength lanthanum carbonate provides serum phosphorus control with a low tablet burden and is preferred by patients and physicians: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Management of hyperphosphatemia, a predictor of mortality in chronic kidney disease, is challenging. Nonadherence to dietary phosphate binders, in part, contributes to uncontrolled serum phosphorus levels. This phase IIIb trial assessed the efficacy of increased dosages (3000 to 4500 mg/d) of reformulated lanthanum carbonate (500-, 750-, and 1000-mg tablets) in nonresponders to dosages of up to 3000 mg/d.
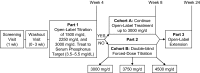
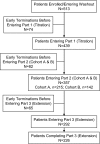
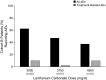
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This 8-wk study with a 4-mo open-label extension enrolled 513 patients who were undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Patients who achieved serum phosphorus control at week 4 with <or=3000 mg/d lanthanum carbonate entered cohort A; nonresponders were randomly assigned to receive 3000, 3750, or 4500 mg/d (cohort B). The primary outcome measure was the control rate for predialysis serum phosphorus levels at the end of week 8, among patients in cohort B.
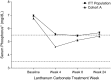
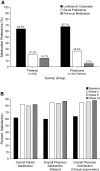
Results: At the end of week 4, 54% of patients achieved serum phosphorus control at dosages <or=3000 mg/d administered as one tablet per meal. Among patients who entered cohort B, control rates of 25, 38, and 32% for patients who were randomly assigned to 3000, 3750, or 4500 mg/d lanthanum carbonate, respectively, were achieved, with no increase in adverse events. Patients and physicians reported significantly higher levels of satisfaction with reformulated lanthanum carbonate compared with previous phosphate binders, partly because of reduced tablet burden with higher dosage strengths. Physicians and patients also expressed a preference for lanthanum carbonate over previous medication.
Conclusions: Reformulated lanthanum carbonate is an effective phosphate binder that may reduce daily tablet burden.
Figures
References
-
- Kalpakian MA, Mehrotra R: Vascular calcification and disordered mineral metabolism in dialysis patients. Semin Dial 20 :139 –143,2007 - PubMed
-
- National Kidney Foundation: K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 42 :S1 –S201,2003 - PubMed
-
- US Renal Data System: Medication use among dialysis patients in the Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Study. United States Renal Data System. Am J Kidney Dis 32 :S60 –S68,1998 - PubMed
-
- Manley HJ, Garvin CG, Drayer DK, Reid GM, Bender WL, Neufeld TK, Hebbar S, Muther RS: Medication prescribing patterns in ambulatory haemodialysis patients: Comparisons of USRDS to a large not-for-profit dialysis provider. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19 :1842 –1848,2004 - PubMed
-
- Tomasello S, Dhupar S, Sherman RA: Phosphate binders, K/DOQI guidelines, and compliance: The unfortunate reality. Dial Transplant 33 :236 –240,2004
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

