Corticotropin-releasing factor in the basolateral amygdala enhances memory consolidation via an interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP pathway: dependence on glucocorticoid receptor activation
- PMID: 18579737
- PMCID: PMC2586417
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1336-08.2008
Corticotropin-releasing factor in the basolateral amygdala enhances memory consolidation via an interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP pathway: dependence on glucocorticoid receptor activation
Abstract
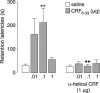
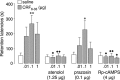
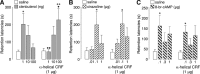
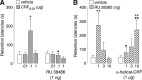
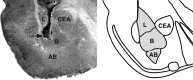
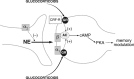
Extensive evidence indicates that stress hormone effects on the consolidation of emotionally influenced memory involve noradrenergic activation of the basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLA). The present experiments examined whether corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) modulates memory consolidation via an interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP system in the BLA. In a first experiment, male Sprague Dawley rats received bilateral infusions of the CRF-binding protein ligand inhibitor CRF(6-33) into the BLA either alone or together with the CRF receptor antagonist alpha-helical CRF(9-41) immediately after inhibitory avoidance training. CRF(6-33) induced dose-dependent enhancement of 48 h retention latencies, which was blocked by coadministration of alpha-helical CRF(9-41), suggesting that CRF(6-33) enhances memory consolidation by displacing CRF from its binding protein, thereby increasing "free" endogenous CRF concentrations. In a second experiment, intra-BLA infusions of atenolol (beta-adrenoceptor antagonist) and Rp-cAMPS (cAMP inhibitor), but not prazosin (alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonist), blocked CRF(6-33)-induced retention enhancement. In a third experiment, the CRF receptor antagonist alpha-helical CRF(9-41) administered into the BLA immediately after training attenuated the dose-response effects of concurrent intra-BLA infusions of clenbuterol (beta-adrenoceptor agonist). In contrast, alpha-helical CRF(9-41) did not alter retention enhancement induced by posttraining intra-BLA infusions of either cirazoline (alpha(1)-adrenoceptor agonist) or 8-br-cAMP (cAMP analog). These findings suggest that CRF facilitates the memory-modulatory effects of noradrenergic stimulation in the BLA via an interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP cascade, at a locus between the membrane-bound beta-adrenoceptor and the intracellular cAMP formation site. Moreover, consistent with evidence that glucocorticoids enhance memory consolidation via a similar interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP cascade, a last experiment found that the CRF and glucocorticoid systems within the BLA interact in influencing beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP effects on memory consolidation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoids interact with the basolateral amygdala beta-adrenoceptor--cAMP/cAMP/PKA system in influencing memory consolidation.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Feb;15(3):553-60. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01876.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11876783
-
Basolateral amygdala noradrenergic influences on memory storage are mediated by an interaction between beta- and alpha1-adrenoceptors.J Neurosci. 1999 Jun 15;19(12):5119-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-12-05119.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10366644 Free PMC article.
-
Orphanin FQ/nociceptin interacts with the basolateral amygdala noradrenergic system in memory consolidation.Learn Mem. 2007 Jan 3;14(1-2):29-35. doi: 10.1101/lm.403607. Print 2007 Jan-Feb. Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17202427 Free PMC article.
-
1999 Curt P. Richter award. Glucocorticoids and the regulation of memory consolidation.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2000 Apr;25(3):213-38. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4530(99)00058-x. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10737694 Review.
-
Role of norepinephrine in mediating stress hormone regulation of long-term memory storage: a critical involvement of the amygdala.Biol Psychiatry. 1999 Nov 1;46(9):1140-52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00157-2. Biol Psychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10560021 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic administration of a β2-adrenergic receptor agonist reduces mechanical allodynia and suppresses the immune response to surgery in a rat model of persistent post-incisional hypersensitivity.Mol Pain. 2021 Jan-Dec;17:1744806921997206. doi: 10.1177/1744806921997206. Mol Pain. 2021. PMID: 33829907 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated stressor exposure enhances contextual fear memory in a beta-adrenergic receptor-dependent process and increases impulsivity in a non-beta receptor-dependent fashion.Physiol Behav. 2015 Oct 15;150:64-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.03.008. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 25747320 Free PMC article.
-
Too much of a good thing: blocking noradrenergic facilitation in medial prefrontal cortex prevents the detrimental effects of chronic stress on cognition.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Mar;38(4):585-95. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.216. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23132268 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin releasing factor-binding protein (CRF-BP) as a potential new therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease and stress disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 22;9(1):272. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0581-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31641098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychophysiological stress response and memory in borderline personality disorder.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2019 Feb 13;10(1):1568134. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2019.1568134. eCollection 2019. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2019. PMID: 30788063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercrombie HC, Speck NS, Monticelli RM. Endogenous cortisol elevations are related to memory facilitation only in individuals who are emotionally aroused. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006;31:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Aldenhoff JB, Gruol DL, Rivier J, Vale W, Siggins GR. Corticotropin releasing factor decreases postburst hyperpolarizations and excites hippocampal neurons. Science. 1983;221:875–877. - PubMed
-
- Asbach S, Schulz C, Lehnert H. Effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone on locus coeruleus neurons in vivo: a microdialysis study using a novel bilateral approach. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001;145:359–363. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–557. - PubMed
-
- Behan DP, Heinrichs SC, Troncoso JC, Liu XJ, Kawas CH, Ling N, De Souza EB. Displacement of corticotropin releasing factor from its binding protein as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995;378:284–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
