Continuous delta-opioid receptor activation reduces neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel (NaV1.7) levels through activation of protein kinase C in painful diabetic neuropathy
- PMID: 18579738
- PMCID: PMC3321315
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5530-07.2008
Continuous delta-opioid receptor activation reduces neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel (NaV1.7) levels through activation of protein kinase C in painful diabetic neuropathy
Abstract
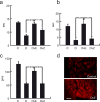
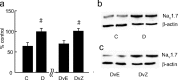
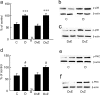
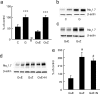
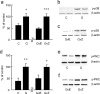
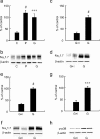
The Na(V)1.7 tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channel isoform plays a critical role in nociception. In rodent models of diabetic neuropathy, increased Na(V)1.7 in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons correlates with the emergence of pain-related behaviors characteristic of painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN). We examined the effect of transgene-mediated expression of enkephalin on pain-related behaviors and their biochemical correlates in DRG neurons. Transfection of DRG neurons by subcutaneous inoculation of a herpes simplex virus-based vector expressing proenkephalin reversed nocisponsive behavioral responses to heat, cold, and mechanical pressure characteristic of PDN. Vector-mediated enkephalin production in vivo prevented the increase in DRG Na(V)1.7 observed in PDN, an effect that correlated with inhibition of phosphorylation of p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and protein kinase C (PKC). Primary DRG neurons in vitro exposed to 45 mm glucose for 18 h also demonstrated an increase in Na(V)1.7 and increased phosphorylation of p38 and PKC; these changes were prevented by transfection in vitro with the enkephalin-expressing vector. The effect of hyperglycemia on Na(V)1.7 production in vitro was mimicked by exposure to PMA and blocked by the myristolated PKC inhibitor 20-28 or the p38 inhibitor SB202190 [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)1H-imidazole]; the effect of vector-mediated enkephalin on Na(V)1.7 levels was prevented by naltrindole. The results of these studies suggest that activation of the presynaptic delta-opioid receptor by enkephalin prevents the increase in neuronal Na(V)1.7 in DRG through inhibition of PKC and p38. These results establish a novel interaction between the delta-opioid receptor and voltage-gated sodium channels.
Figures
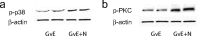
Similar articles
-
Reduction of voltage gated sodium channel protein in DRG by vector mediated miRNA reduces pain in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy.Mol Pain. 2012 Mar 22;8:17. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-17. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 22439790 Free PMC article.
-
Vector-mediated release of GABA attenuates pain-related behaviors and reduces Na(V)1.7 in DRG neurons.Eur J Pain. 2011 Oct;15(9):913-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2011.03.007. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Eur J Pain. 2011. PMID: 21486703 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of sodium channel Na(v)1.8 by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase increases current density in dorsal root ganglion neurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Mar 19;28(12):3190-201. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4403-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18354022 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory action of protein kinase Cbeta inhibitor on tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ current in small dorsal root ganglion neurons in diabetic rats.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Apr 24;417(1):90-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.040. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17339081
-
Roles of Voltage-Gated Tetrodotoxin-Sensitive Sodium Channels NaV1.3 and NaV1.7 in Diabetes and Painful Diabetic Neuropathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 5;17(9):1479. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091479. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27608006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetic painful and insensate neuropathy: pathogenesis and potential treatments.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Oct;6(4):638-47. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.07.004. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19789069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Neuroprotection.Front Neurosci. 2018 Apr 20;12:196. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00196. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29731703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of subtypes γ and ε of protein kinase C in colon pain induced by formalin injection.Neurosignals. 2011;19(3):142-50. doi: 10.1159/000328311. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Neurosignals. 2011. PMID: 21701146 Free PMC article.
-
The Na(V)1.7 sodium channel: from molecule to man.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Jan;14(1):49-62. doi: 10.1038/nrn3404. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23232607 Review.
-
Reduction of voltage gated sodium channel protein in DRG by vector mediated miRNA reduces pain in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy.Mol Pain. 2012 Mar 22;8:17. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-17. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 22439790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren SC, Levine JD. Protein kinase C inhibitors decrease hyperalgesia and C-fiber hyperexcitability in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:684–692. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Liu S, Tanaka M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. Changes in the expression of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels within dorsal root ganglia neurons in inflammatory pain. Pain. 2004;108:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Calcutt NA. Potential mechanisms of neuropathic pain in diabetes. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2002;50:205–228. - PubMed
-
- Calcutt NA, Jorge MC, Yaksh TL, Chaplan SR. Tactile allodynia and formalin hyperalgesia in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of insulin, aldose reductase inhibition and lidocaine. Pain. 1996;68:293–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
