TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control
- PMID: 18579750
- PMCID: PMC2492741
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1664408
TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control
Abstract
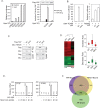
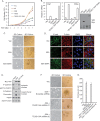
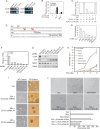
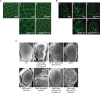
The YAP transcription coactivator has been implicated as an oncogene and is amplified in human cancers. Recent studies have established that YAP is phosphorylated and inhibited by the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway. Here we demonstrate that the TEAD family transcription factors are essential in mediating YAP-dependent gene expression. TEAD is also required for YAP-induced cell growth, oncogenic transformation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. CTGF is identified as a direct YAP target gene important for cell growth. Moreover, the functional relationship between YAP and TEAD is conserved in Drosophila Yki (the YAP homolog) and Scalloped (the TEAD homolog). Our study reveals TEAD as a new component in the Hippo pathway playing essential roles in mediating biological functions of YAP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Both TEAD-binding and WW domains are required for the growth stimulation and oncogenic transformation activity of yes-associated protein.Cancer Res. 2009 Feb 1;69(3):1089-98. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2997. Epub 2009 Jan 13. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19141641
-
Targeting YAP/TAZ-TEAD signaling as a therapeutic approach in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2025 Mar 1;612:217467. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217467. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 39826667
-
Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Jul 28;19(8):996-1002. doi: 10.1038/ncb3581. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28752853 Free PMC article.
-
The TEAD Family and Its Oncogenic Role in Promoting Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 21;17(1):138. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010138. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26805820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippo pathway inhibition by blocking the YAP/TAZ-TEAD interface: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Dec;28(12):867-873. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1549226. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 30482112 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual role of YAP and TAZ in renewal of the intestinal epithelium.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;17(1):7-19. doi: 10.1038/ncb3084. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25531778
-
FOXP4 Is a Direct YAP1 Target That Promotes Gastric Cancer Stemness and Drives Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 4;84(21):3574-3588. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-3074. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39047223 Free PMC article.
-
RBM8A, a new target of TEAD4, promotes breast cancer progression by regulating IGF1R and IRS-2.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 4;22(1):823. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05639-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39232805 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Governing Cardiomyocyte Differentiation.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;15(6):798. doi: 10.3390/genes15060798. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP oncogene overexpression supercharges colon cancer proliferation.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 15;11(6):1090-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.6.19453. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22356765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basu S., Totty N.F., Irwin M.S., Sudol M., Downward J. Akt phosphorylates the Yes-associated protein, YAP, to induce interaction with 14–3–3 and attenuation of p73-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Camargo F.D., Gokhale S., Johnnidis J.B., Fu D., Bell G.W., Jaenisch R., Brummelkamp T.R. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
-
- Debnath J., Muthuswamy S.K., Brugge J.S. Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods. 2003;30:256–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
