Joint engagement and the emergence of language in children with autism and Down syndrome
- PMID: 18581223
- PMCID: PMC2640949
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-008-0601-7
Joint engagement and the emergence of language in children with autism and Down syndrome
Abstract
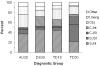
Systematic longitudinal observations were made as typically developing toddlers and young children with autism and with Down syndrome interacted with their caregivers in order to document how joint engagement developed over a year-long period and how variations in joint engagement experiences predicted language outcome. Children with autism displayed a persistent deficit in coordinated joint attention; children with Down syndrome were significantly less able to infuse symbols into joint engagement. For all groups, variations in amount of symbol-infused supported joint engagement, a state in which the child attended to a shared object and to language but not actively to the partner, contributed to differences in expressive and receptive language outcome, over and above initial language capacity.
Figures
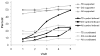
References
-
- Adamson LB. Communication development during infancy. Boulder, CO: Westview; 1996.
-
- Adamson LB, Bakeman R. Mothers’ communicative actions: Changes during infancy. Infant Behavior and Development. 1984;7:467–478.
-
- Adamson LB, Bakeman R. The development of shared attention during infancy. In: Vasta R, editor. Annals of Child Development. 8 . London: Kingsley; 1991. pp. 1–41.
-
- Adamson LB, Bakeman R. The development of displaced speech in early mother-child conversations. Child Development. 2006;77:186–200. - PubMed
-
- Adamson LB, Bakeman R, Deckner DF. The development of symbol-infused joint engagement. Child Development. 2004;75:1171–1187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

