A case of ischemic colitis associated with the herbal food supplement ma huang
- PMID: 18581601
- PMCID: PMC2615353
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.3.496
A case of ischemic colitis associated with the herbal food supplement ma huang
Abstract
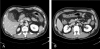
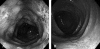
Ischemic colitis is a condition that usually occurs in the elderly, as a form of vascular disease. However, ischemic colitis also occurs, though rarely, in healthy young adults. Moreover, food supplements containing Ephedra sinica or ma huang have been linked to adverse central nervous and cardiovascular events. A 40-year-old man was admitted to our emergency department after 2 episodes of abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea that lasted 24 hours. His medical history was unremarkable for risk factors of bowel ischemia, except for well-controlled hypertension. However, a weight-loss supplement, Ephedra sinica, had been prescribed for daily use during the previous month. Both abdominal/pelvic computed tomography and colonoscopy revealed findings compatible with ischemic colitis. His conditions spontaneously improved without any serious complications, and he was advised to discontinue the use of herbal medications containing ephedrine. In this paper, we describe a case of ischemic colitis that was potentially linked to the use of ma huang with a review of the relevant literature.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adverse cardiovascular and central nervous system events associated with dietary supplements containing ephedra alkaloids.N Engl J Med. 2000 Dec 21;343(25):1833-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200012213432502. N Engl J Med. 2000. PMID: 11117974
-
Ephedra-containing dietary supplements in the US versus ephedra as a Chinese medicine.Am J Chin Med. 2004;32(1):1-10. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X04001680. Am J Chin Med. 2004. PMID: 15154280 Review.
-
Protective effect of gui zhi (Ramulus Cinnamomi) on abnormal levels of four amino acid neurotransmitters by chronically ma huang (Herb Ephedra) intoxicated prefrontal cortex in rats treated with a ma huang-gui zhi herb pair.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;249:112408. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112408. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31751653
-
[The false positive reaction of the Triage panel drug-of-abuse by herbal drugs ma-huang (Ephedra sinica (Ephedraceae))].Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 2001 Nov;55(3):331-8. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11905042 Japanese.
-
Acute hepatitis associated with the use of a Chinese herbal product, ma-huang.Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Jul;91(7):1436-8. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996. PMID: 8678010 Review.
Cited by
-
ACG clinical guideline: epidemiology, risk factors, patterns of presentation, diagnosis, and management of colon ischemia (CI).Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan;110(1):18-44; quiz 45. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2014.395. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25559486 No abstract available.
References
-
- MacDonald PH. Ischaemic colitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;16:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Pittler MH, Schmidt K, Ernst E. Adverse events of herbal food supplements for body weight reduction: systematic review. Obes Rev. 2005;6:93–111. - PubMed
-
- Haller CA, Benowitz NL. Adverse cardiovascular and central nervous system events associated with dietary supplements containing ephedra alkaloids. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1833–1838. - PubMed
-
- Ryan CK, Reamy B, Rochester JA. Ischemic colitis associated with herbal product use in a young woman. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2002;15:309–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

