Localization of electrogenic Na/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 variants in rat brain
- PMID: 18582537
- PMCID: PMC2711903
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.037
Localization of electrogenic Na/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 variants in rat brain
Abstract
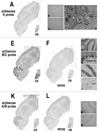
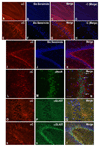
The activity of HCO(3)(-) transporters contributes to the acid-base environment of the nervous system. In the present study, we used in situ hybridization, immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunogold electron microscopy to localize electrogenic Na/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 splice variants (-A, -B, and -C) in rat brain. The in situ hybridization data are consistent with NBCe1-B and -C, but not -A, being the predominant NBCe1 variants in brain, particularly in the cerebellum, hippocampus, piriform cortex, and olfactory bulb. An antisense probe to the B and C variants strongly labeled granule neurons in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, and cells in the granule layer and Purkinje layer (e.g. Bergmann glia) of the cerebellum. Weaker labeling was observed in the pyramidal layer of the hippocampus and in astrocytes throughout the brain. Similar, but weaker labeling was obtained with an antisense probe to the A and B variants. In immunoblot studies, antibodies to the A and B variants (alphaA/B) and C variant (alphaC) labeled approximately 130-kDa proteins in various brain regions. From immunohistochemistry data, both alphaA/B and alphaC exhibited diffuse labeling throughout brain, but alphaA/B labeling was more intracellular and punctate. Based on co-localization studies with antibodies to neuronal or astrocytic markers, alphaA/B labeled neurons in the pyramidal layer and dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, as well as cortex. alphaC labeled glia surrounding neurons (and possibly neurons) in the neuropil of the Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum, the pyramidal cell layer and dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, and the cortex. According to electron microscopy data from the cerebellum, alphaA/B primarily labeled neurons intracellularly and alphaC labeled astrocytes at the plasma membrane. In summary, the B and C variants are the predominant NBCe1 variants in rat brain and exhibit different localization profiles.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Distinct expression and subcellular localization patterns of Na+/HCO3- cotransporter (SLC 4A4) variants NBCe1-A and NBCe1-B in mouse brain.Neuroscience. 2007 May 25;146(3):1220-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.061. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17433553
-
Na/HCO3 cotransporters in rat brain: expression in glia, neurons, and choroid plexus.J Neurosci. 2000 Sep 15;20(18):6839-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-06839.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10995828 Free PMC article.
-
Variants of the electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCe1) in mouse hippocampal neurons are regulated by extracellular pH changes: evidence for a Rab8a-dependent mechanism.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;45(7):1427-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23583738
-
Expression of the B splice variant of NBCe1 (SLC4A4) in the mouse kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):F417-F428. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00515.2017. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29631353 Free PMC article.
-
Na-coupled bicarbonate transporters of the solute carrier 4 family in the nervous system: function, localization, and relevance to neurologic function.Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 29;171(4):951-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.037. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20884330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Cl- -HCO3- exchanger AE3 in intracellular pH homeostasis in cultured murine hippocampal neurons, and in crosstalk to adjacent astrocytes.J Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;595(1):93-124. doi: 10.1113/JP272470. Epub 2016 Nov 6. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27353306 Free PMC article.
-
The divergence, actions, roles, and relatives of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters.Physiol Rev. 2013 Apr;93(2):803-959. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00023.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23589833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transcriptome-based assessment of the astrocytic dystrophin-associated complex in the developing human brain.J Neurosci Res. 2018 Feb;96(2):180-193. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24082. Epub 2017 May 16. J Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 28509351 Free PMC article.
-
Towards bridging the gap between acid-base transporters and neuronal excitability modulation.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 15;6(4):221-5. eCollection 2014. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25755844 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Ion Channels and Transporters and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia.Aging Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(4):1748-1770. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1201. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38300642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aalkjær C, Frische S, Leipziger J, Nielsen S, Praetorius J. Sodium coupled bicarbonate transporters in the kidney, an update. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004;181:505–512. - PubMed
-
- Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Boorer K, Pushkin A, Kurtz I. Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and functional expression of the human pancreatic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 1998a;273:17689–17695. - PubMed
-
- Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Pushkin A, Kurtz I. Axial heterogeneity of sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter expression in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1998b;274:F628–F633. - PubMed
-
- Berger UV, Hediger MA. Differential distribution of the glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in tanycytes of the third ventricle. J Comp Neurol. 2001;433:101–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

