Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates intestinal epithelial focal adhesion kinase synthesis via Smad- and p38-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 18583311
- PMCID: PMC2475776
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070729
Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates intestinal epithelial focal adhesion kinase synthesis via Smad- and p38-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
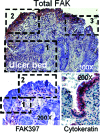
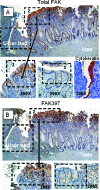
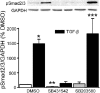
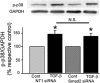
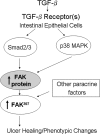
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) regulates cell migration, proliferation, and apoptosis. FAK protein is reduced at the edge of migrating gut epithelial sheets in vitro, but it has not been characterized in restitutive gut mucosa in vivo. Here we show that FAK and activated phospho-FAK (FAK(397)) immunoreactivity was lower in epithelial cells immediately adjacent to human gastric and colonic ulcers in vivo, but dramatically increased in epithelia near the ulcers, possibly reflecting stimulation by growth factors absent in vitro. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, but not fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, or vascular endothelial growth factor, increased FAK levels in Caco-2 and IEC-6 cells. Epithelial immunoreactivity to TGF-beta and phospho-Smad3 was also higher near the ulcers, varying in parallel with FAK. The TGF-beta receptor antagonist SB431542 completely blocked TGF-beta-induced Smad2/3 and p38 activation in IEC-6 cells. SB431542, the p38 antagonist SB203580, and siRNA-mediated reduction of Smad2 and p38alpha prevented TGF-beta stimulation of both FAK transcription and translation (as measured via a FAK promoter-luciferase construct). FAK(397) levels were directly related to total FAK protein expression. Although gut epithelial motility is associated with direct inhibition of FAK protein adjacent to mucosal wounds, TGF-beta may increase FAK protein near but not bordering mucosal ulcers via Smad2/3 and p38 signals. Our results show that regulation of FAK expression may be as important as FAK phosphorylation in critically influencing gut epithelial cell migration after mucosal injury.
Figures
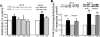



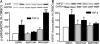
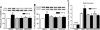

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targeting of the focal adhesion complex prevents oncogenic TGF-beta signaling and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R68. doi: 10.1186/bcr2360. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19740433 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced extracellular matrix with a novel inhibitor of the TGF-beta type I receptor kinase activity: SB-431542.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;62(1):58-64. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.1.58. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12065755
-
The Src family kinase inhibitors PP2 and PP1 block TGF-beta1-mediated cellular responses by direct and differential inhibition of type I and type II TGF-beta receptors.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011 May;11(4):524-35. doi: 10.2174/156800911795538075. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21395548
-
Transforming growth factor-β signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2017-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770288 Review.
-
Bone marrow Schwann cells induce hematopoietic stem cell hibernation.Int J Hematol. 2014 Jun;99(6):695-8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1588-9. Epub 2014 May 10. Int J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24817152 Review.
Cited by
-
ZINC40099027 Promotes Gastric Mucosal Repair in Ongoing Aspirin-Associated Gastric Injury by Activating Focal Adhesion Kinase.Cells. 2021 Apr 15;10(4):908. doi: 10.3390/cells10040908. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33920786 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 treatment is associated with prohibitin expression in the Crohn's disease intestinal fibrosis mouse model.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:617145. doi: 10.1155/2013/617145. Epub 2013 Apr 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23690666 Free PMC article.
-
The P-loop region of Schlafen 3 acts within the cytosol to induce differentiation of human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1843(12):3029-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.017. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25261706 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta1 modulates focal adhesion kinase expression in rat intestinal epithelial IEC-6 cells via stimulatory and inhibitory Smad binding elements.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Feb;1789(2):88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.11.002. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19059368 Free PMC article.
-
Gut homeostasis, injury, and healing: New therapeutic targets.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 May 7;28(17):1725-1750. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i17.1725. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35633906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burridge K, Nuckolls G, Otey C, Pavalko F, Simon K, Turner C. Actin-membrane interaction in focal adhesions. Cell Differ Dev. 1990;32:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Salazar EP, Rozengurt E. Bombesin and platelet-derived growth factor induce association of endogenous focal adhesion kinase with Src in intact Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:28371–28378. - PubMed
-
- Yu CF, Basson MD. Matrix-specific FAK and MAPK reorganization during Caco-2 cell motility. Microsc Res Tech. 2000;51:191–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

