An experimental model of acute humoral rejection of renal allografts associated with concomitant cellular rejection
- PMID: 18583312
- PMCID: PMC2475773
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070391
An experimental model of acute humoral rejection of renal allografts associated with concomitant cellular rejection
Abstract
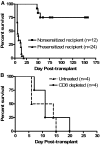
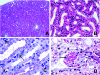
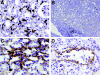
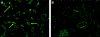
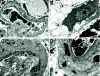
Acute humoral rejection (AHR), which occurs in up to 8% of kidney transplant recipients, is a significant cause of renal allograft dysfunction and loss. More efficacious treatment modalities are needed to eliminate or curtail alloantibody production and its deleterious effects on the kidney. The availability of animal models mimicking human AHR is essential to understand its pathophysiology and develop new treatment strategies. Using a mouse kidney transplant model, we demonstrate that presensitization of recipients with donor skin grafts results in rejection of subsequent renal allografts. All presensitized mice developed renal failure 8.6 +/- 4.3 days after engraftment, with serum creatinine values near 100 micromol/dl. Graft histology revealed mild, diffuse, interstitial, mononuclear cell infiltrates; prominent peritubular capillary inflammatory cell margination; patchy interstitial hemorrhage; interstitial edema; and focal glomerular fibrin deposition. Complement (C3d) deposition was diffuse and prominent in peritubular capillaries. Serum analysis demonstrated high levels of circulating alloantibodies with broad cross-reactivity to many MHC haplotypes. The clinical setting and histological findings of our model strongly resemble AHR, which is frequently associated with cellular rejection, a situation commonly encountered in human renal allograft recipients. This animal model provides a valuable tool to study the pathogenesis of AHR, its relationship to cellular alloimmunity, its contribution to graft injury, and the effects of various potential therapeutic interventions.
Figures

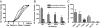
Similar articles
-
Acute humoral rejection of renal allografts in CCR5(-/-) recipients.Am J Transplant. 2008 Mar;8(3):557-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.02125.x. Am J Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18294152
-
A Model of Acute Antibody-Mediated Renal Allograft Rejection in the Sensitized Rata.Exp Clin Transplant. 2018 Jun;16(3):294-300. doi: 10.6002/ect.2016.0316. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Exp Clin Transplant. 2018. PMID: 28760115
-
Platelets and capillary injury in acute humoral rejection of renal allografts.Hum Pathol. 2003 Jun;34(6):533-40. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(03)00189-8. Hum Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12827606
-
Pathology of C4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection in renal allografts.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013 Jun;18(3):319-26. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e32835d4daf. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23283250 Review.
-
Humoral rejection in kidney transplantation: new concepts in diagnosis and treatment.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002 Nov;11(6):609-18. doi: 10.1097/00041552-200211000-00007. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002. PMID: 12394606 Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptive immunity rather than viral cytopathology mediates polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in mice.Am J Transplant. 2012 Jun;12(6):1419-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04005.x. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Am J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22420885 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized ATP Suppresses B Lymphocyte Activity to Attenuate Antibody-mediated Rejection of Kidney Allografts in Mice.Transplantation. 2025 Jan 1;109(1):e11-e21. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000005118. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Transplantation. 2025. PMID: 38946027 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Model Established by Early Renal Transplantation After Skin Allograft Sensitization Mimics Clinical Antibody-Mediated Rejection.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 4;9:1356. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01356. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30022978 Free PMC article.
-
Can mouse kidney transplant models inform mechanisms of injury and acceptance in clinical kidney transplantation?Am J Transplant. 2025 Jul;25(7):1391-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2025.04.001. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Am J Transplant. 2025. PMID: 40209906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-Suppressor CXCR5+CD8+ T Cells Are More Potent Regulators of Humoral Alloimmunity after Kidney Transplant in Mice Compared to CD4+ Regulatory T Cells.J Immunol. 2024 May 1;212(9):1504-1518. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300289. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38517294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins AB, Schneeberger EE, Pascual MA, Saidman SL, Williams WW, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Cosimi AB, Colvin RB. Complement activation in acute humoral renal allograft rejection: diagnostic significance of C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:2208–2214. - PubMed
-
- Crespo M, Pascual M, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Mauiyyedi S, Collins AB, Fitzpatrick D, Farrell ML, Williams WW, Delmonico FL, Cosimi AB, Colvin RB, Saidman SL. Acute humoral rejection in renal allograft recipients: I. Incidence, serology and clinical characteristics. Transplantation. 2001;71:652–658. - PubMed
-
- Mauiyyedi S, Crespo M, Collins AB, Schneeberger EE, Pascual MA, Saidman SL, Tolkoff-Rubin NE, Williams WW, Delmonico FL, Cosimi AB, Colvin RB. Acute humoral rejection in kidney transplantation: II. Morphology, immunopathology, and pathologic classification. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:779–787. - PubMed
-
- Böhmig GA, Exner M, Watschinger B, Regele H. Acute humoral renal allograft rejection. Curr Opin Urol. 2002;12:95–99. - PubMed
-
- Lederer SR, Kluth-Pepper B, Schneeberger H, Albert E, Land W, Feucht HE. Impact of humoral alloreactivity early after transplantation on the long-term survival of renal allografts. Kidney Int. 2001;59:334–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

