MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries
- PMID: 18583537
- PMCID: PMC2847579
- DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0356
MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries
Abstract
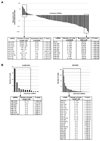
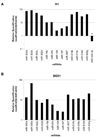
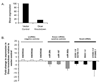
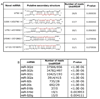
We used massively parallel pyrosequencing to discover and characterize microRNAs (miRNAs) expressed in human embryonic stem cells (hESC). Sequencing of small RNA cDNA libraries derived from undifferentiated hESC and from isogenic differentiating cultures yielded a total of 425,505 high-quality sequence reads. A custom data analysis pipeline delineated expression profiles for 191 previously annotated miRNAs, 13 novel miRNAs, and 56 candidate miRNAs. Further characterization of a subset of the novel miRNAs in Dicer-knockdown hESC demonstrated Dicer-dependent expression, providing additional validation of our results. A set of 14 miRNAs (9 known and 5 novel) was noted to be expressed in undifferentiated hESC and then strongly downregulated with differentiation. Functional annotation analysis of predicted targets of these miRNAs and comparison with a null model using non-hESC-expressed miRNAs identified statistically enriched functional categories, including chromatin remodeling and lineage-specific differentiation annotations. Finally, integration of our data with genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation data on OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG binding sites implicates these transcription factors in the regulation of nine of the novel/candidate miRNAs identified here. Comparison of our results with those of recent deep sequencing studies in mouse and human ESC shows that most of the novel/candidate miRNAs found here were not identified in the other studies. The data indicate that hESC express a larger complement of miRNAs than previously appreciated, and they provide a resource for additional studies of miRNA regulation of hESC physiology. Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest is found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Mimeault M, Hauke R, Batra SK. Stem cells: a revolution in therapeutics-recent advances in stem cell biology and their therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Sep;82(3):252–264. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004 Jul;5(7):522–531. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000 Feb 24;403(6772):901–906. - PubMed
-
- Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA, Nakahara K, Carthew RW, Ruohola-Baker H. Stem cell division is regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature. 2005 Jun 16;435(7044):974–978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12 CA076930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 CA009515-21/22/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA80416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG004059/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083867/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM081619/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 K12 CA076930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA080416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES07033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM069983/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 CA09657-16/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

