Prostasin: a possible candidate gene for human hypertension
- PMID: 18583984
- PMCID: PMC3812941
- DOI: 10.1038/ajh.2008.224
Prostasin: a possible candidate gene for human hypertension
Abstract
Background: Prostasin, a serine protease, is suggested to be a novel mechanism regulating the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) expressed in the distal nephron. This study aimed to evaluate whether the human prostasin gene is a novel candidate gene underlying blood pressure (BP) elevation.
Methods: In a sample of healthy African-American (AA) and European-American (EA) twin subjects aged 17.6 +/- 3.3 years (n = 920, 45% AAs), race-specific tagging single-nucleotide polymorphisms (tSNPs) were identified to tag all the available SNPs +/- 2 kb up- and downstream of the prostasin gene from HapMap at r2 of 0.8-1.0. Selection yielded four tSNPs in AAs and one in EAs, with one tSNP (rs12597511: C to T) present in both AAs and EAs.
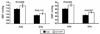
Results: For rs12597511, CT and TT genotypes exhibited higher systolic BP (SBP) than CC genotype (115.9 +/- 1.1 mm Hg vs. 113.7 +/- 0.6 mm Hg, P = 0.025 (AAs); and 110.7 +/- 0.5 mm Hg vs. 109.6 +/- 0.6 mm Hg, P = 0.115 (EAs)). CT and TT genotypes compared with CC genotype showed a significant increase in diastolic BP (DBP) in both racial groups (62.5 +/- 0.7 mm Hg vs. 60.4 +/- 0.4 mm Hg, P = 0.003 (AAs); and 58.2 +/- 0.3 mm Hg vs. 56.7 +/- 0.4 mm Hg, P = 0.007 (EAs)). Furthermore, there was an increase in radial pulse wave velocity (PWV) in subjects with CT and TT genotype as compared with those with CC genotype (6.5 +/- 0.1 vs. 6.1 +/- 0.1 m/s, P < 0.0001) (EAs); and 6.7 +/- 0.1 vs. 6.6 +/- 0.1 m/s, P = 0.354 (AAs)). Analyses combining AAs and EAs consistently demonstrated a statistical significance of rs12597511 on all the phenotypes including SBP/DBP and PWV.
Conclusion: Genetic variation of the prostasin gene may be implicated in the development of hypertension in youths..
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Persu A, Barbry P, Bassilana F, Houot AM, Mengual R, Lazdunski M, Corvol P, Jeunemaitre X. Genetic analysis of the beta subunit of the epithelial Na+ channel in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1998;32:129–137. - PubMed
-
- Baker EH, Dong YB, Sagnella GA, Rothwell M, Onipinla AK, Markandu ND, Cappuccio FP, Cook DG, Persu A, Corvol P, Jeunemaitre X, Carter ND, MacGregor GA. Association of hypertension with T594M mutation in beta subunit of epithelial sodium channels in black people resident in London. Lancet. 1998;351:1388–1392. - PubMed
-
- Persu A, Coscoy S, Houot AM, Corvol P, Barbry P, Jeunemaitre X. Polymorphisms of the gamma subunit of the epithelial Na+ channel in essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999;17:639–645. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosius WT, Bloem LJ, Zhou L, Rebhun JF, Snyder PM, Wagner MA, Guo C, Pratt JH. Genetic variants in the epithelial sodium channel in relation to aldosterone and potassium excretion and risk for hypertension. Hypertension. 1999;34:631–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

