Sepsid even-skipped enhancers are functionally conserved in Drosophila despite lack of sequence conservation
- PMID: 18584029
- PMCID: PMC2430619
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000106
Sepsid even-skipped enhancers are functionally conserved in Drosophila despite lack of sequence conservation
Abstract
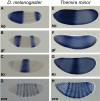
The gene expression pattern specified by an animal regulatory sequence is generally viewed as arising from the particular arrangement of transcription factor binding sites it contains. However, we demonstrate here that regulatory sequences whose binding sites have been almost completely rearranged can still produce identical outputs. We sequenced the even-skipped locus from six species of scavenger flies (Sepsidae) that are highly diverged from the model species Drosophila melanogaster, but share its basic patterns of developmental gene expression. Although there is little sequence similarity between the sepsid eve enhancers and their well-characterized D. melanogaster counterparts, the sepsid and Drosophila enhancers drive nearly identical expression patterns in transgenic D. melanogaster embryos. We conclude that the molecular machinery that connects regulatory sequences to the transcription apparatus is more flexible than previously appreciated. In exploring this diverse collection of sequences to identify the shared features that account for their similar functions, we found a small number of short (20-30 bp) sequences nearly perfectly conserved among the species. These highly conserved sequences are strongly enriched for pairs of overlapping or adjacent binding sites. Together, these observations suggest that the local arrangement of binding sites relative to each other is more important than their overall arrangement into larger units of cis-regulatory function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Wray GA. The evolutionary significance of cis-regulatory mutations. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:206–216. - PubMed
-
- Costas J, Casares F, Vieira J. Turnover of binding sites for transcription factors involved in early Drosophila development. Gene. 2003;310:215–220. - PubMed
-
- Dermitzakis ET, Bergman CM, Clark AG. Tracing the evolutionary history of Drosophila regulatory regions with models that identify transcription factor binding sites. Mol Biol Evol. 2003;20:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Dermitzakis ET, Clark AG. Evolution of transcription factor binding sites in Mammalian gene regulatory regions: conservation and turnover. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:1114–1121. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig MZ, Bergman C, Patel NH, Kreitman M. Evidence for stabilizing selection in a eukaryotic enhancer element. Nature. 2000;403:564–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

