Modulation of TNF release by choline requires alpha7 subunit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated signaling
- PMID: 18584048
- PMCID: PMC2435495
- DOI: 10.2119/2008-00079.Parrish
Modulation of TNF release by choline requires alpha7 subunit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated signaling
Abstract
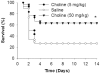
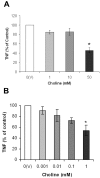
The alpha7 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7nAChR) is an essential component in the vagus nerve-based cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway that regulates the levels of TNF, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), and other cytokines during inflammation. Choline is an essential nutrient, a cell membrane constituent, a precursor in the biosynthesis of acetylcholine, and a selective natural alpha7nAChR agonist. Here, we studied the anti-inflammatory potential of choline in murine endotoxemia and sepsis, and the role of the alpha7nAChR in mediating the suppressive effect of choline on TNF release. Choline (0.1-50 mM) dose-dependently suppressed TNF release from endotoxin-activated RAW macrophage-like cells, and this effect was associated with significant inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Choline (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneally [i.p.]) treatment prior to endotoxin administration in mice significantly reduced systemic TNF levels. In contrast to its TNF suppressive effect in wild type mice, choline (50 mg/kg, i.p.) failed to inhibit systemic TNF levels in alpha7nAChR knockout mice during endotoxemia. Choline also failed to suppress TNF release from endotoxin-activated peritoneal macrophages isolated from alpha7nAChR knockout mice. Choline treatment prior to endotoxin resulted in a significantly improved survival rate as compared with saline-treated endotoxemic controls. Choline also suppressed HMGB1 release in vitro and in vivo, and choline treatment initiated 24 h after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced polymicrobial sepsis significantly improved survival in mice. In addition, choline suppressed TNF release from endotoxin-activated human whole blood and macrophages. Collectively, these data characterize the anti-inflammatory efficacy of choline and demonstrate that the modulation of TNF release by choline requires alpha7nAChR-mediated signaling.
Figures



References
-
- Tracey KJ, et al. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986;234:470–4. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002;420:853–9. - PubMed
-
- Borovikova LV, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 2000;405:458–62. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature. 2003;421:384–8. - PubMed
-
- Huston JM, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation reduces serum high mobility group box 1 levels and improves survival in murine sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2762–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

