Chronic allograft nephropathy
- PMID: 18584214
- PMCID: PMC2697362
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-008-0869-z
Chronic allograft nephropathy
Abstract
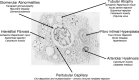
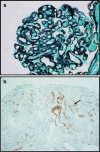
Chronic allograft nephropathy (CAN) is the leading cause of renal allograft loss in paediatric renal transplant recipients. CAN is the result of immunological and nonimmunological injury, including acute rejection episodes, hypoperfusion, ischaemia reperfusion, calcineurin toxicity, infection and recurrent disease. The development of CAN is often insidious and may be preceded by subclinical rejection in a well-functioning allograft. Classification of CAN is histological using the Banff classification of renal allograft pathology with classic findings of interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, glomerulosclerosis, fibrointimal hyperplasia and arteriolar hyalinosis. Although improvement in immunosuppression has led to greater 1-year graft survival rates, chronic graft loss remains relatively unchanged and opportunistic infectious complications remain a problem. Protocol biopsy monitoring is not current practice in paediatric transplantation for CAN monitoring but may have a place if new treatment options become available. Newer immunosuppression regimens, closer monitoring of the renal allograft and management of subclinical rejection may lead to reduced immune injury leading to CAN in the paediatric population but must be weighed against the risk of increased immunosuppression and calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC, Cavallo T, Croker BP, Demetris AJ, Drachenberg CB, Fogo AB, Furness P, Gaber LW, Gibson IW, Glotz D, Goldberg JC, Grande J, Halloran PF, Hansen HE, Hartley B, Hayry PJ, Hill CM, Hoffman EO, Hunsicker LG, Lindblad AS, Yamaguchi Y. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int. 1999;55:713–723. - PubMed
-
- Isoniemi H, Taskinen E, Hayry P. Histological chronic allograft damage index accurately predicts chronic renal allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1994;58:1195–1198. - PubMed
-
- Solez K, Axelsen RA, Benediktsson H, Burdick JF, Cohen AH, Colvin RB, Croker BP, Droz D, Dunnill MS, Halloran PF. International standardization of criteria for the histologic diagnosis of renal allograft rejection: the Banff working classification of kidney transplant pathology. Kidney Int. 1993;44:411–422. - PubMed
-
- Nickeleitt V, Zeiler M, Gudat F, Thiel G, Mihatsch MJ. Detection of the complement degradation product C4d in renal allografts: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:242–251. - PubMed

