The effect of phosphorylation on the electron capture dissociation of peptide ions
- PMID: 18585055
- PMCID: PMC2570175
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jasms.2008.05.015
The effect of phosphorylation on the electron capture dissociation of peptide ions
Abstract
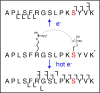
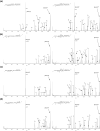
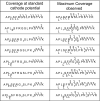
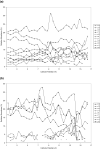
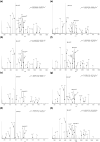
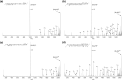
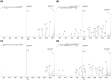
The effect of site and frequency of phosphorylation on the electron capture dissociation of peptide ions has been investigated. The ECD of a suite of synthetic peptides (APLSFRGSLPKSYVK; one unmodified, three singly-phosphorylated, three-doubly phosphorylated, and one triply-phosphorylated); two tryptic phosphopeptides (YKVPQLEIVPN(p)SAEER, alpha-casein and FQ(p)SEEQQQTEDELQDK, beta-casein) and their unmodified counterparts, were determined over a range of ECD cathode potentials. The results show that, for doubly-charged precursor ions, the presence of phosphorylation has a deleterious effect on ECD sequence coverage. The fragmentation patterns observed suggest that for peptides with multiple basic residues, the phospho-groups exist in their deprotonated form and form salt-bridges with protonated amino acid side chains. The fragmentation observed for the acidic tryptic peptides suggested the presence of noncovalent interactions, which were perturbed on phosphorylation. Increasing the ECD electron energy significantly improves sequence coverage. Alternatively, improved sequence coverage can be achieved by performing ECD on triply-charged precursor ions. The findings are important for the understanding of gas-phase fragmentation of phosphopeptides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Phosphorylation on Electron Capture Dissociation of Proteins: A Top-Down Perspective.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017 Sep;28(9):1805-1814. doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1710-3. Epub 2017 Jul 6. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28685494 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the electron capture dissociation fragmentation behavior of doubly and triply protonated peptides from trypsin, Glu-C, and chymotrypsin digestion.J Proteome Res. 2008 Jul;7(7):2834-44. doi: 10.1021/pr800038y. Epub 2008 Jun 13. J Proteome Res. 2008. PMID: 18549259
-
Effects of the position of internal histidine residues on the collision-induced fragmentation of triply protonated tryptic peptides.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2001 Dec;12(12):1262-71. doi: 10.1016/S1044-0305(01)00312-9. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2001. PMID: 11766753
-
The radical ion chemistry of S-nitrosylated peptides.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012 Dec;23(12):2063-74. doi: 10.1007/s13361-012-0492-x. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012. PMID: 23055078
-
Electron capture dissociation of singly and multiply phosphorylated peptides.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2000;14(19):1793-800. doi: 10.1002/1097-0231(20001015)14:19<1793::AID-RCM95>3.0.CO;2-Q. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2000. PMID: 11006587
Cited by
-
Effects of acidic peptide size and sequence on trivalent praseodymium adduction and electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2017 Apr;52(4):218-229. doi: 10.1002/jms.3919. J Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28170125 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Phosphorylation on Electron Capture Dissociation of Proteins: A Top-Down Perspective.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017 Sep;28(9):1805-1814. doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1710-3. Epub 2017 Jul 6. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28685494 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of phosphorylated nucleotides by collisional and electron-based tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016 Oct 15;30(19):2155-63. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7701. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016. PMID: 27479882 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale localization of protein phosphorylation by use of electron capture dissociation mass spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 May;8(5):904-12. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800451-MCP200. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19131326 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the electron capture dissociation mass spectrometry of phosphopeptides with traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulations.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015 Jun;26(6):1004-13. doi: 10.1007/s13361-015-1094-1. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 25832028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zubarev R.A., Kelleher N.L., McLafferty F.W. Electron Capture Dissociation of Multiply Charged Protein Cations: A Nonergodic Process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120(13):3265–3266.
-
- Baba T., Hashimoto Y., Hasegawa H., Hirabayashi A., Waki I. Electron Capture Dissociation in a Radio Frequency Ion Trap. Anal. Chem. 2004;76(15):4263–4266. - PubMed
-
- Silivra O.A., Kjeldsen F., Ivonin I.A., Zubarev R.A. Electron capture dissociation of polypeptides in a three-dimensional quadrupole ion trap: Implementation and first results. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005;16(1):22–27. - PubMed
-
- Ding L., Brancia F.L. Electron Capture Dissociation in a Digital Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006;78(6):1995–2000. - PubMed
-
- Syrstad E.A., Turecek F. Toward a General Mechanism of Electron Capture Dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005;16(2):208–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

