Mechanism of local and global Ca2+ sensing by calmodulin in complex with a Ca2+ channel
- PMID: 18585356
- PMCID: PMC4262405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.025
Mechanism of local and global Ca2+ sensing by calmodulin in complex with a Ca2+ channel
Abstract
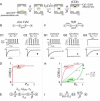
Calmodulin (CaM) in complex with Ca(2+) channels constitutes a prototype for Ca(2+) sensors that are intimately colocalized with Ca(2+) sources. The C-lobe of CaM senses local, large Ca(2+) oscillations due to Ca(2+) influx from the host channel, and the N-lobe senses global, albeit diminutive Ca(2+) changes arising from distant sources. Though biologically essential, the mechanism underlying global Ca(2+) sensing has remained unknown. Here, we advance a theory of how global selectivity arises, and we experimentally validate this proposal with methodologies enabling millisecond control of Ca(2+) oscillations seen by the CaM/channel complex. We find that global selectivity arises from rapid Ca(2+) release from CaM combined with greater affinity of the channel for Ca(2+)-free versus Ca(2+)-bound CaM. The emergence of complex decoding properties from the juxtaposition of common elements, and the techniques developed herein, promise generalization to numerous molecules residing near Ca(2+) sources.
Figures





Comment in
-
Rescuing a failing heart: think globally, treat locally.Nat Med. 2009 Jan;15(1):25-6. doi: 10.1038/nm0109-25. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19129780 No abstract available.
References
-
- Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K. Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron. 2003;40:331–346. - PubMed
-
- Bayley P, Ahlstrom P, Martin SR, Forsen S. The kinetics of calcium binding to calmodulin: Quin 2 and ANS stopped-flow fluorescence studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120:185–191. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Black DJ, Halling DB, Mandich DV, Pedersen SE, Altschuld RA, Hamilton SL. Calmodulin interactions with IQ peptides from voltage-dependent calcium channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288:C669–676. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Lipp P, Berridge MJ. The organisation and functions of local Ca(2+) signals. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:2213–2222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

