NOD-like receptors (NLRs): bona fide intracellular microbial sensors
- PMID: 18585455
- PMCID: PMC2572576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.06.001
NOD-like receptors (NLRs): bona fide intracellular microbial sensors
Abstract
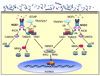
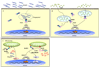
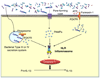
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor (NLR) (nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing) family of proteins has been demonstrated to function as regulators of innate immune response against microbial pathogens. Stimulation of NOD1 and NOD2, two prototypic NLRs, results in the activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB. On the other hand, a different set of NLRs induces caspase-1 activation through the assembly of an inflammasome. This review discusses recent findings regarding the signaling pathways utilized by NLR proteins in the control of caspase-1 and NF-kappaB activation, as well as the nonredundant role of NLRs in pathogen clearance. The review also covers advances regarding the cellular localization of these proteins and the implications this may have on pathogen sensing and signal transduction.
Figures
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Inohara, Chamaillard, McDonald C, Nuñez G. NOD-LRR proteins: role in host-microbial interactions and inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:355–383. - PubMed
-
- Derry WB, Putzke AP, Rothman JH. Caenorhabditis elegans p53: role in apoptosis, meiosis, and stress resistance. Science. 2001;294:591–595. - PubMed
-
- Liu QA, Hengartner MO. The molecular mechanism of programmed cell death in C. elegans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;887:92–104. - PubMed
-
- Inohara N, Koseki T, Lin J, del Peso L, Lucas PC, Chen FF, Ogura Y, Nunez G. An induced proximity model for NF-kappa B activation in the Nod1/RICK and RIP signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27823–27831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

