Efficient algorithms for accurate hierarchical clustering of huge datasets: tackling the entire protein space
- PMID: 18586742
- PMCID: PMC2718652
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn174
Efficient algorithms for accurate hierarchical clustering of huge datasets: tackling the entire protein space
Abstract
Motivation: UPGMA (average linking) is probably the most popular algorithm for hierarchical data clustering, especially in computational biology. However, UPGMA requires the entire dissimilarity matrix in memory. Due to this prohibitive requirement, UPGMA is not scalable to very large datasets.
Application: We present a novel class of memory-constrained UPGMA (MC-UPGMA) algorithms. Given any practical memory size constraint, this framework guarantees the correct clustering solution without explicitly requiring all dissimilarities in memory. The algorithms are general and are applicable to any dataset. We present a data-dependent characterization of hardness and clustering efficiency. The presented concepts are applicable to any agglomerative clustering formulation.
Results: We apply our algorithm to the entire collection of protein sequences, to automatically build a comprehensive evolutionary-driven hierarchy of proteins from sequence alone. The newly created tree captures protein families better than state-of-the-art large-scale methods such as CluSTr, ProtoNet4 or single-linkage clustering. We demonstrate that leveraging the entire mass embodied in all sequence similarities allows to significantly improve on current protein family clusterings which are unable to directly tackle the sheer mass of this data. Furthermore, we argue that non-metric constraints are an inherent complexity of the sequence space and should not be overlooked. The robustness of UPGMA allows significant improvement, especially for multidomain proteins, and for large or divergent families.
Availability: A comprehensive tree built from all UniProt sequence similarities, together with navigation and classification tools will be made available as part of the ProtoNet service. A C++ implementation of the algorithm is available on request.
Figures





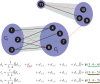
 and ⊕ notations.
and ⊕ notations.
 , as long as d7,9 is missing.
, as long as d7,9 is missing.Similar articles
-
On the quality of tree-based protein classification.Bioinformatics. 2005 May 1;21(9):1876-90. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti244. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15647305
-
Cross-over between discrete and continuous protein structure space: insights into automatic classification and networks of protein structures.PLoS Comput Biol. 2009 Mar;5(3):e1000331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000331. Epub 2009 Mar 27. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19325884 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale clustering of protein sequences with FORCE -A layout based heuristic for weighted cluster editing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Oct 17;8:396. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-396. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17941985 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting fold novelty based on ProtoNet hierarchical classification.Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 1;21(7):1020-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti135. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15539447
-
Large-scale protein clustering in the age of deep learning.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2025 Jun 14;94:103078. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2025.103078. Online ahead of print. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2025. PMID: 40517452 Review.
Cited by
-
Clustering Acoustic Segments Using Multi-Stage Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 30;10(10):e0141756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141756. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26517376 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-fast sequence clustering from similarity networks with SiLiX.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Apr 22;12:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-116. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21513511 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics: A Primer on Processing Workflow and Analysis.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2022 Apr;43(2):142-146. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2022.02.003. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2022. PMID: 35339254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrafast clustering algorithms for metagenomic sequence analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2012 Nov;13(6):656-68. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs035. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Brief Bioinform. 2012. PMID: 22772836 Free PMC article.
-
A novel hierarchical clustering algorithm for gene sequences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Jul 23;13:174. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-174. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22823405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D'haeseleer P. How does gene expression clustering work? Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1499–1501. - PubMed
-
- Durbin R, et al. Biological Sequence Analysis : Probabilistic Models of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1999.

