POIMs: positional oligomer importance matrices--understanding support vector machine-based signal detectors
- PMID: 18586746
- PMCID: PMC2718648
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn170
POIMs: positional oligomer importance matrices--understanding support vector machine-based signal detectors
Abstract
Motivation: At the heart of many important bioinformatics problems, such as gene finding and function prediction, is the classification of biological sequences. Frequently the most accurate classifiers are obtained by training support vector machines (SVMs) with complex sequence kernels. However, a cumbersome shortcoming of SVMs is that their learned decision rules are very hard to understand for humans and cannot easily be related to biological facts.
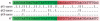
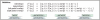
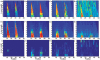
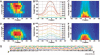
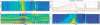
Results: To make SVM-based sequence classifiers more accessible and profitable, we introduce the concept of positional oligomer importance matrices (POIMs) and propose an efficient algorithm for their computation. In contrast to the raw SVM feature weighting, POIMs take the underlying correlation structure of k-mer features induced by overlaps of related k-mers into account. POIMs can be seen as a powerful generalization of sequence logos: they allow to capture and visualize sequence patterns that are relevant for the investigated biological phenomena.
Availability: All source code, datasets, tables and figures are available at http://www.fml.tuebingen.mpg.de/raetsch/projects/POIM.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures

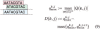

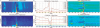
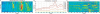
Similar articles
-
SVM-Fold: a tool for discriminative multi-class protein fold and superfamily recognition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 May 22;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S4-S2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17570145 Free PMC article.
-
Profile-based string kernels for remote homology detection and motif extraction.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2005 Jun;3(3):527-50. doi: 10.1142/s021972000500120x. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2005. PMID: 16108083
-
ARTS: accurate recognition of transcription starts in human.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 15;22(14):e472-80. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl250. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16873509
-
Biological applications of support vector machines.Brief Bioinform. 2004 Dec;5(4):328-38. doi: 10.1093/bib/5.4.328. Brief Bioinform. 2004. PMID: 15606969 Review.
-
An overview of the wcd EST clustering tool.Bioinformatics. 2008 Jul 1;24(13):1542-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn203. Epub 2008 May 14. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18480101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring sequence characteristics related to high-level production of secreted proteins in Aspergillus niger.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045869. Epub 2012 Oct 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049690 Free PMC article.
-
KIRMES: kernel-based identification of regulatory modules in euchromatic sequences.Bioinformatics. 2009 Aug 15;25(16):2126-33. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp278. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19389732 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of diffusion coefficients from voltammetric signals by support vector and gaussian process regression.J Cheminform. 2014 May 28;6:30. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-30. eCollection 2014. J Cheminform. 2014. PMID: 24987463 Free PMC article.
-
Improving HIV coreceptor usage prediction in the clinic using hints from next-generation sequencing data.Bioinformatics. 2012 Sep 15;28(18):i589-i595. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts373. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22962486 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable machine learning for genomics.Hum Genet. 2022 Sep;141(9):1499-1513. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02387-9. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34669035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barash Y, et al. Modeling depend. in protein-DNA binding sites. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference in Computational Molecular Biology (RECOMB).2003.
-
- Ben-Gal I, et al. Identification of transcription factor binding sites with variable-order bayesian networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2657–2666. - PubMed
-
- Chen T-M, et al. Prediction of splice sites with dependency graphs and their expanded bayesian networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:471–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

