Activation of AMPK attenuates neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of acute lung injury
- PMID: 18586954
- PMCID: PMC2536800
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90210.2008
Activation of AMPK attenuates neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of acute lung injury
Abstract
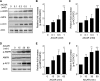
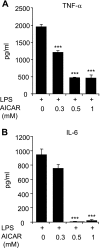
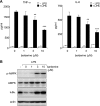
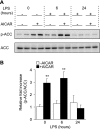
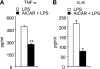
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is activated by increases in the intracellular AMP-to-ATP ratio and plays a central role in cellular responses to metabolic stress. Although activation of AMPK has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, there is little information concerning the role that AMPK may play in modulating neutrophil function and neutrophil-dependent inflammatory events, such as acute lung injury. To examine these issues, we determined the effects of pharmacological activators of AMPK, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-d-ribofuranoside (AICAR) and barberine, on Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-induced neutrophil activation. AICAR and barberine dose-dependently activated AMPK in murine bone marrow neutrophils. Exposure of LPS-stimulated neutrophils to AICAR or barberine inhibited release of TNF-alpha and IL-6, as well as degradation of IkappaBalpha and nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB, compared with findings in neutrophil cultures that contained LPS without AICAR or barberine. Administration of AICAR to mice resulted in activation of AMPK in the lungs and was associated with decreased severity of LPS-induced lung injury, as determined by diminished neutrophil accumulation in the lungs, reduced interstitial pulmonary edema, and diminished levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. These results suggest that AMPK activation reduces TLR4-induced neutrophil activation and diminishes the severity of neutrophil-driven proinflammatory processes, including acute lung injury.
Figures

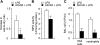
References
-
- Abraham E Alterations in cell signaling in sepsis. Clin Infect Dis 41, Suppl 7: S459–S464, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E Neutrophils and acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 31: S195–S199, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E NF-kappaB activation. Crit Care Med 28: N100–N104, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey KJ. HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165: 2950–2954, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Carmody A, Shenkar R, Arcaroli J. Neutrophils as early immunologic effectors in hemorrhage- or endotoxemia-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279: L1137–L1145, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

