Simple method for plating Escherichia coli bacteriophages forming very small plaques or no plaques under standard conditions
- PMID: 18586961
- PMCID: PMC2519272
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00306-08
Simple method for plating Escherichia coli bacteriophages forming very small plaques or no plaques under standard conditions
Abstract
The use of low concentrations (optimally 2.5 to 3.5 microg/ml, depending on top agar thickness) of ampicillin in the bottom agar of the plate allows for formation of highly visible plaques of bacteriophages which otherwise form extremely small plaques or no plaques on Escherichia coli lawns. Using this method, we were able to obtain plaques of newly isolated bacteriophages, propagated after induction of prophages present in six E. coli O157:H(-) strains which did not form plaques when standard plating procedures were employed.
Figures
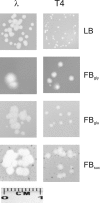


Similar articles
-
A sensitive and simple plaque formation method for the Stx2 phage of Escherichia coli O157:H7, which does not form plaques in the standard plating procedure.Plasmid. 2012 May;67(3):227-35. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Plasmid. 2012. PMID: 22186359
-
Application of bacteriophages to control intestinal Escherichia coli O157:H7 levels in ruminants.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Aug;72(8):5359-66. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00099-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16885287 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of lytic bacteriophages against enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli.J Appl Microbiol. 2011 May;110(5):1323-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04989.x. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Appl Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21362115
-
An improved plaque assay for poor plaque-producing temperate lactococcal bacteriophages.J Appl Microbiol. 1997 Jul;83(1):85-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00193.x. J Appl Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9246774
-
Methods for the detection and isolation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli.Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2000;(29):133S-143S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2000.tb05341.x. Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10880188 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Assessment of Phage and Linezolid Based Implant Coatings for Treatment of Methicillin Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) Mediated Orthopaedic Device Related Infections.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0157626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157626. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27333300 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Layer Agar (DLA) Modifications for the First Step of the Phage-Antibiotic Synergy (PAS) Identification.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;10(11):1306. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111306. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827244 Free PMC article.
-
Novel ZnO-binding peptides obtained by the screening of a phage display peptide library.J Nanopart Res. 2012 Nov;14(11):1218. doi: 10.1007/s11051-012-1218-5. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Nanopart Res. 2012. PMID: 23193370 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage Procurement for Therapeutic Purposes.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 12;7:1177. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01177. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27570518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streamlining standard bacteriophage methods for higher throughput.MethodsX. 2018 Jan 31;5:159-172. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2018.01.007. eCollection 2018. MethodsX. 2018. PMID: 30622914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedon, S. T. 1999. Bacteriophage T4 resistance to lysis-inhibition collapse. Genet. Res. 74:1-11. - PubMed
-
- Abedon, S. T., and R. R. Culler. 2007. Bacteriophage evolution given spatial constraint. J. Theor. Biol. 248:111-119. - PubMed
-
- Allison, H. E., M. J. Sergeant, C. E. James, J. R. Saunders, D. L. Smith, R. J. Sharp, T. S. Marks, and A. J. McCarthy. 2003. Immunity profiles of wild-type and recombinant Shiga-like toxin-encoding bacteriophages and characterization of novel double lysogens. Infect. Immun. 71:3409-3418. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, L. J., P. Thomen, T. Makushok, and D. Chatenay. 2006. Propagation of fluorescent viruses in growing plaques. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 96:615-621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

